Recently, American Bitcoin – a digital asset mining and management company co-founded by Eric Trump and Donald Trump Jr. – announced the purchase of an additional 1,414 Bitcoins worth approximately $163 million.
With this deal, the total amount of Bitcoin that American Bitcoin is holding has increased to 3,865 BTC, equivalent to 445 million USD at current market price (about 114,802 USD/ BTC).
- Eric Trump, the company’s Chief Strategy Officer, said their goal is to increase the amount of Bitcoin per share – a key indicator of a company’s true value to shareholders. “We believe the most important measure of the success of a Bitcoin accumulation platform is the amount of Bitcoin that is actually backed by each share,” he stressed.
- American Bitcoin launched in March 2025, after cryptocurrency mining company Hut 8 transferred most of its Bitcoin mining equipment in exchange for a controlling stake. After just a few months of operation, the company went public on the Nasdaq in early September under the ticker symbol “ABTC.”
- On its first day of trading, American Bitcoin shares rose more than 16%, despite trading being halted five times due to wild price swings, at one point surging as much as 85% during the session.
- Prior to the listing, American Bitcoin completed a merger with Gryphon Digital Mining, a Las Vegas-based Bitcoin mining company. Shareholders of both parties approved the stock-for-stock merger, thereby solidifying American Bitcoin’s position as an ambitious “new player” in the digital asset mining market.
- Gryphon shares surged more than 230% during the merger preparations – a sign of high investor expectations for the American Bitcoin brand.
- The development of American Bitcoin comes as President Donald Trump has taken an increasingly friendly stance towards digital assets. He is not only a Bitcoin supporter but also directly involved in investing and issuing policies aimed at “making the United States a global center for cryptocurrency mining and trading.”
- However, some of his recent decisions have sparked fierce controversy in Washington, notably the pardon of Changpeng “CZ” Zhao, the founder of Binance, who was convicted of violating US anti-money laundering laws.
- The move has drawn sharp criticism from many Democratic lawmakers. Maxine Waters described it as “shocking but not surprising,” saying that President Trump is “giving preferential treatment to cryptocurrency criminals.”
However, observers say Trump's decision is part of a strategy to encourage the development of the domestic blockchain industry, while attracting foreign Capital in the renewable energy sector for Bitcoin mining - a field he mentioned during his election campaign.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #Jucom #Bitcoin #BitcoinMining


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-10-28 07:53
📣 Trump's Bitcoin Mining Company Just Bought Another $163 Million in BTC.
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
- US Representative Ro Khanna is expected to introduce a resolution today that would stop the President, his family members, and members of Congress from trading crypto or stocks and accepting foreign funds.
- The proposal comes amid growing public outrage over President Donald Trump’s decision to pardon Binance founder Changpeng Zhao. It also points to a broader frustration with politicians and their ability to trade while occupying positions of power.
Khanna Targets Crypto Trading in Congress
- California Representative Ro Khanna is set to unveil a Congressional resolution today to prevent the President and Members of Congress from trading cryptocurrencies and accepting foreign money.
- Khanna first announced the initiative over the weekend. Since then, he has used social media and televised interviews to explain his reasoning behind this move.
“We have a president who is enriching himself and his family in an obscene wealth that is unprecedented in American history. People need to wake up to what’s going on– it’s corruption right before our very eyes,” Khanna told MSNBC.
- The California representative has long advocated for banning stock trading by politicians and prohibiting campaign contributions from PACs and lobbyists. This new measure appears prompted by Trump’s recent decision to grant a prominent crypto figure clemency.
Trump’s Binance Pardon Fuels Political Backlash
- Last week, Trump pardoned Binance founder Changpeng Zhao (CZ) for violating US anti-money laundering laws.
- Some welcomed the news, viewing the case against CZ as an example of unfair treatment toward the crypto industry. Others, however, saw it as a political move and a calculated effort by Binance to win the President’s favor.
- Khanna aligned himself with the latter view.
“You’ve got a foreign billionaire who was basically engaged in money laundering, having money go to Hamas, Iran, [and] child abusers. He was convicted and served four [months] in prison. And then he petitions for a pardon… and what he does is he says, ‘I’m going to support World Liberty’… which they’re making millions of dollars on while Donald Trump is President,” he explained in another MSNBC interview.
Despite these public remarks, Khanna’s office has not yet released the detailed text of the proposed legislation.
What distinguishes Khanna from other critical Democrats is his generally positive outlook on cryptocurrencies.
Growing Scrutiny Over Politics and Crypto
- Stand With Crypto, a crypto advocacy group closely affiliated with Coinbase, currently lists Khanna as a politician who is “strongly supportive” of cryptocurrency.
- The California representative’s A-grade sharply contrasts with some of his Democratic colleagues and outspoken critics of the President’s connections to the crypto industry. For instance, Senator Elizabeth Warren and fellow Californian Representative Maxine Waters hold F-grades.
- Despite his favorable view of crypto and its underlying technology, Khanna has generally advocated for a clear separation between the industry’s influence and politics.
- This sentiment has recently grown stronger among the public as Trump’s ties to the crypto industry have expanded.
- Trump’s campaign and affiliated PACs have received millions in donations from the crypto industry, while his family-backed venture, World Liberty Financial, has launched its own stablecoin. The company has also reportedly been involved in a crypto-related deal with the UAE that coincided with the country receiving more favorable US AI chip technology access.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #Jucom #US #CryptoTrading


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-10-28 08:00
🔥 U.S Rep Pushes To Ban Crypto Trading For Presidents and Congress Members!
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
- Tech giant IBM has just announced the launch of a cryptocurrency platform dedicated to financial institutions and the US government, marking one of the company's strongest moves in the field of digital assets and blockchain infrastructure.
- According to the latest announcement, this platform is called “Digital Asset Haven”, expected to be officially deployed in the fourth quarter of 2025 under the software-as-a-service (SaaS) model. IBM has partnered with Dfns, a leading provider of secure cryptocurrency wallets, to build this system.
“Digital Asset Haven” – a turning point for digital asset infrastructure in the US
- IBM claims the new platform will provide crypto custody and settlement services to U.S. businesses and government organizations. The main goal is to simplify the integration of digital assets into the traditional financial system — something many banks and large corporations are looking for amid the boom in Tokenize and stablecoins.
- A highlight of Digital Asset Haven is its ability to connect directly to over 40 public blockchain networks, allowing organizations to access onchain yield from decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols safely and legally.
- Additionally, the platform is designed to meet complex Token compliance requirements, including governance, identity verification, and anti-money laundering (AML) — all consolidated within the same IBM-managed ecosystem.
- The rapid growth of stablecoins and Tokenize real assets (RWA) is driving strong demand for institutional-grade blockchain infrastructure solutions, according to IBM.
Large banks, hedge funds, and financial institutions are moving from “experimental” to “real deployment” as they see the potential for cost savings and increased transaction speeds.
Clarisse Hagège, CEO of Dfns, Chia :
“In order for digital assets to be integrated into banking systems and Capital markets, the underlying infrastructure must be at the same level as the traditional financial system. Together with IBM, we have built a platform that goes beyond custody to orchestrate the entire digital asset ecosystem, paving the way for global scale.”
Tokenize asset market grows explosively
- According to the latest data from Binance Research, the number of Tokenize stocks increased by more than 220% in July 2025 alone, mimicking the 2020–2021 DeFi boom, when TVL increased from $1 billion to $100 billion in just two years.
- Also in July, the number of blockchain wallets holding Tokenize stocks increased from 1,600 to more than 90,000 addresses, indicating a surge in demand for investing in digital securities.
- At the RWA Summit 2025 in Cannes, Sergey Nazarov, co-founder of Chainlink, said that blockchain-based compliance tools could make traditional transactions “10 times faster and significantly cheaper” than the legacy financial system.
- On June 30, Chainlink also announced the Automated Compliance Engine (ACE) — a modular standards framework that enables organizations to manage legal compliance on the blockchain, aiming to unlock over $100 trillion in new Capital for the digital asset economy.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #Jucom #IBM #CryptoExchange


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-10-28 07:56
📣 Tech giant IBM launches Crypto platform dedicated to organizations.
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
- One of Iran’s largest private banks has fallen into bankruptcy, with the assets of more than 42 million customers being absorbed by the Iranian state-owned lender, Bank Melli.
- Ayandeh Bank declared bankruptcy on Thursday after it accumulated $5.1 billion in losses and nearly $3 billion in debt, local media outlet Iran International reported on Friday.
- The bankruptcy was declared days after the Central Bank of Iran failed to rescue the bank, leaving officials with no option but to close it, which had operated 270 branches nationwide.
- More than 42 million customers were affected, Iran News Update reported.
While CBI Governor Mohammad Reza Farzin assured Ayandeh customers that they will be able to recover their savings immediately, the incident highlights the risk involved in trusting banks that lend out customer deposits, operate with fractional reserves and seek bailouts when things go wrong.
Failures in the banking system were seemingly one of Satoshi Nakamoto’s motivations for creating Bitcoin, as evidenced by a message embedded in Bitcoin's genesis block that references the UK government bailing out banks.
Meanwhile, one of the catalysts of Bitcoin growth in the last few years was the US local banking crisis in early 2023, where Silicon Valley Bank, Signature Bank, and Silvergate Bank filed for bankruptcy or were forced into liquidation.
Bitcoin’s price rallied from below $20,000 to over $29,000 in that month as public trust in the US banking system waned.
Earlier this month, Reuters — citing a report from Morningstar — noted that regional US banks were still showing signs of financial stress despite boosting reserves and customer deposits since March 2023.
Eight Iranian banks are at risk of dissolution
- Iran’s banking system has become fragile due to widespread sanctions, which block access to international financial networks, restrict US dollar transactions and heighten risks in the local banking sector while the Iranian rial continues to lose purchasing power.
- Earlier this year, the Central Bank warned that eight other local banks risk dissolution unless they implement reforms.
- Iranian crypto exchanges haven’t been without problems either, as Nobitex suffered an $81 million hack in June.
- It was one of the biggest contributors to Iranian crypto flows falling 11% up until July amid a series of conflicts with Israel.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain#IranianBank #Jucom #CentralBank


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-10-27 09:45
📣 Major Iranian private bank goes bankrupt, roiling 42M customers!📛
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
- Bitcoin’s (BTC) Stock-to-Flow (S2F) model, one of the most widely cited BTC valuation frameworks, forecasts a peak price of $222,000 during this market cycle, but investors should exercise caution when using the model, according to André Dragosch, the European head of research at investment firm Bitwise.
- The Stock-to-Flow model does not take into account demand-side factors, and instead, centers its price modeling on Bitcoin’s halvings, which reduce the amount of newly issued BTC by half every four years, Dragosch said.
He added:
“Today, institutional demand via Bitcoin exchange-traded products (ETPs) and treasury holdings outweighs the annualized supply reduction from the latest Halving by more than seven times.”
Exchange-traded funds, ETPs, and other Bitcoin investment vehicles have created a price floor for BTC, supporting prices above the $100,000 level.
Crypto Investors and analysts continue to debate the price of Bitcoin during the current market cycle and whether BTC has topped out, or still has room to run, as the market structure matures due to the presence of institutional investors.
Analysts debate how high BTC can go in this market cycle
- Bitcoin can still reach $200,000 by the end of 2025, according to Geoff Kendrick, the global head of digital assets research at Standard Chartered, a pro-crypto bank.
- The flash crash in October that took BTC down to under $104,000 might present a buying opportunity for investors, who could drive BTC to new highs.
- Other analysts forecast a BTC price as much as $500,000 in 2026, driven by an explosion of the M2 money supply, a metric tracking the total amount of US dollars in existence globally.
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #Investors #Jucom #Bitcoin


Lee | Ju.Com
2025-10-27 09:41
🔶 Investors should be 'cautious' when using BTC stock-to-flow model!
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What Is the Total Number of Transactions on the Bitcoin Network?
Understanding the total number of transactions on the Bitcoin network is essential for grasping how active and widely used this pioneering cryptocurrency truly is. This metric offers insights into user engagement, network health, and overall adoption trends. In this article, we will explore what influences transaction volume, recent developments in 2023, and what these figures mean for investors and users alike.
How Does Transaction Volume Reflect Network Activity?
The total number of Bitcoin transactions indicates how frequently users are transferring funds or engaging with blockchain-based applications. On average, as of 2023, around 250,000 to 300,000 transactions occur daily. These fluctuations are driven by various factors such as market sentiment—bullish periods tend to see increased activity—as well as regulatory environments that can either encourage or restrict usage.
High transaction volumes suggest a vibrant ecosystem where users actively buy, sell, or transfer Bitcoin. Conversely, dips may signal reduced interest or external pressures like stricter regulations. Monitoring these numbers helps stakeholders gauge whether Bitcoin remains a popular medium for peer-to-peer payments or speculative trading.
Factors Influencing Transaction Counts
Several key elements impact how many transactions are recorded on the blockchain:
- Market Conditions: Bull markets often lead to increased trading activity as investors seek opportunities.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter laws can temporarily suppress transaction volumes; conversely, favorable policies may boost activity.
- Network Congestion: When many users transact simultaneously—such as during major price swings—transaction fees rise due to limited block space.
- Technological Developments: Improvements like SegWit (Segregated Witness) have optimized transaction processing times and costs over time.
These factors collectively shape daily transaction counts and influence user behavior across different periods.
Recent Trends in 2023: Fluctuations in Transaction Numbers
In April 2023, the Bitcoin network experienced a notable surge in transaction volume driven by heightened market speculation amid potential regulatory shifts in major economies. This increase was partly fueled by traders reacting to news about possible government interventions that could impact cryptocurrency markets globally.
However, May saw an uptick in average transaction fees—about a 20% rise compared to previous months—which reflects higher network congestion. Elevated fees can discourage smaller transactions from occurring frequently because they become less cost-effective for everyday use cases like micro-payments or casual transfers.
These recent trends highlight how external events directly influence not only how much activity occurs but also its economic viability for typical users.
Blockchain Size and Its Impact on Transactions
The size of the Bitcoin blockchain itself provides context about overall network activity; it stood at approximately 400 GB in early 2023—a significant increase from previous years due to continuous addition of new blocks containing transactional data.
A larger blockchain signifies more historical data stored across nodes worldwide but also raises concerns regarding scalability:
- Larger blockchains require more storage capacity.
- Synchronization times increase for new nodes joining the network.
- Higher data loads can contribute to slower confirmation times during peak periods unless scaling solutions are implemented effectively.
Efforts such as Lightning Network aim to address these scalability challenges by enabling faster off-chain transactions while maintaining security through underlying blockchain settlement layers.
The Role of Miners and Validation Processes
Miners play a crucial role in maintaining accurate records by validating transactions through complex computational puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work (PoW). They compete within seconds to add new blocks containing pending transactions onto the chain; successful miners receive rewards plus associated fees paid by transacting parties.
This validation process ensures integrity but is energy-intensive: estimates suggest that mining consumes substantial electricity globally. As demand increases with higher transaction volumes during active periods like April-May 2023’s surge,
the environmental footprint becomes more prominent concern among regulators and advocates alike.
Key Points About Mining:
- Miners validate hundreds of thousands of daily transactions
- Validation ensures decentralization & security
- Rising demand impacts energy consumption
Regulatory Environment's Effect on Transaction Volumes
Government policies significantly influence user participation levels on the Bitcoin network. In early 2023,
several countries introduced stricter regulations targeting crypto exchanges,which temporarily dampened trading activities reflected through decreased transaction counts initially observed after policy announcements.
However,
some jurisdictions adopted clearer frameworks encouraging institutional involvement,potentially stabilizing or increasing future transactional activity once compliance mechanisms were established.
Summary:
Regulatory uncertainty remains one of the most unpredictable factors affecting total bitcoin transactions; ongoing legislative developments will continue shaping usage patterns moving forward.
Future Outlook: Scalability Solutions & Adoption Trends
As interest grows among retail investors and institutions alike,
scalability solutions such as Taproot upgrades,Lightning Network implementations,and sidechains aim to facilitate faster processing at lower costs.
These technological advancements could help sustain higher throughput levels necessary for mainstream adoption while reducing congestion-related fee hikes seen earlier this year.
Moreover,
wider acceptance from merchants accepting bitcoin payments directly enhances real-world utility beyond speculative trading,
potentially leading toward sustained growth in total number of daily transactions over coming years.
By continuously monitoring metrics like total bitcoin transaction count alongside technological improvements and regulatory changes,
stakeholders—from individual users to large-scale investors—can better understand market dynamics
and make informed decisions aligned with evolving industry conditions.
References
- CoinDesk — General information on Bitcoin networks
- Blockchain.com Charts — Historical data analysis
- Blockchain Size Data — Blockchain growth insights
- Transaction Fees & Congestion — Impact analysis
- Bitcoin Mining Process — Technical validation overview
- Regulatory Impact Reports — Policy effects assessment
Understanding how many people transact using Bitcoin provides valuable insight into its current state—and future potential—as both an investment asset and a decentralized payment system amidst an ever-changing global landscape


Lo
2025-05-06 07:37
What is the total number of transactions on the Bitcoin network?
What Is the Total Number of Transactions on the Bitcoin Network?
Understanding the total number of transactions on the Bitcoin network is essential for grasping how active and widely used this pioneering cryptocurrency truly is. This metric offers insights into user engagement, network health, and overall adoption trends. In this article, we will explore what influences transaction volume, recent developments in 2023, and what these figures mean for investors and users alike.
How Does Transaction Volume Reflect Network Activity?
The total number of Bitcoin transactions indicates how frequently users are transferring funds or engaging with blockchain-based applications. On average, as of 2023, around 250,000 to 300,000 transactions occur daily. These fluctuations are driven by various factors such as market sentiment—bullish periods tend to see increased activity—as well as regulatory environments that can either encourage or restrict usage.
High transaction volumes suggest a vibrant ecosystem where users actively buy, sell, or transfer Bitcoin. Conversely, dips may signal reduced interest or external pressures like stricter regulations. Monitoring these numbers helps stakeholders gauge whether Bitcoin remains a popular medium for peer-to-peer payments or speculative trading.
Factors Influencing Transaction Counts
Several key elements impact how many transactions are recorded on the blockchain:
- Market Conditions: Bull markets often lead to increased trading activity as investors seek opportunities.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter laws can temporarily suppress transaction volumes; conversely, favorable policies may boost activity.
- Network Congestion: When many users transact simultaneously—such as during major price swings—transaction fees rise due to limited block space.
- Technological Developments: Improvements like SegWit (Segregated Witness) have optimized transaction processing times and costs over time.
These factors collectively shape daily transaction counts and influence user behavior across different periods.
Recent Trends in 2023: Fluctuations in Transaction Numbers
In April 2023, the Bitcoin network experienced a notable surge in transaction volume driven by heightened market speculation amid potential regulatory shifts in major economies. This increase was partly fueled by traders reacting to news about possible government interventions that could impact cryptocurrency markets globally.
However, May saw an uptick in average transaction fees—about a 20% rise compared to previous months—which reflects higher network congestion. Elevated fees can discourage smaller transactions from occurring frequently because they become less cost-effective for everyday use cases like micro-payments or casual transfers.
These recent trends highlight how external events directly influence not only how much activity occurs but also its economic viability for typical users.
Blockchain Size and Its Impact on Transactions
The size of the Bitcoin blockchain itself provides context about overall network activity; it stood at approximately 400 GB in early 2023—a significant increase from previous years due to continuous addition of new blocks containing transactional data.
A larger blockchain signifies more historical data stored across nodes worldwide but also raises concerns regarding scalability:
- Larger blockchains require more storage capacity.
- Synchronization times increase for new nodes joining the network.
- Higher data loads can contribute to slower confirmation times during peak periods unless scaling solutions are implemented effectively.
Efforts such as Lightning Network aim to address these scalability challenges by enabling faster off-chain transactions while maintaining security through underlying blockchain settlement layers.
The Role of Miners and Validation Processes
Miners play a crucial role in maintaining accurate records by validating transactions through complex computational puzzles—a process known as proof-of-work (PoW). They compete within seconds to add new blocks containing pending transactions onto the chain; successful miners receive rewards plus associated fees paid by transacting parties.
This validation process ensures integrity but is energy-intensive: estimates suggest that mining consumes substantial electricity globally. As demand increases with higher transaction volumes during active periods like April-May 2023’s surge,
the environmental footprint becomes more prominent concern among regulators and advocates alike.
Key Points About Mining:
- Miners validate hundreds of thousands of daily transactions
- Validation ensures decentralization & security
- Rising demand impacts energy consumption
Regulatory Environment's Effect on Transaction Volumes
Government policies significantly influence user participation levels on the Bitcoin network. In early 2023,
several countries introduced stricter regulations targeting crypto exchanges,which temporarily dampened trading activities reflected through decreased transaction counts initially observed after policy announcements.
However,
some jurisdictions adopted clearer frameworks encouraging institutional involvement,potentially stabilizing or increasing future transactional activity once compliance mechanisms were established.
Summary:
Regulatory uncertainty remains one of the most unpredictable factors affecting total bitcoin transactions; ongoing legislative developments will continue shaping usage patterns moving forward.
Future Outlook: Scalability Solutions & Adoption Trends
As interest grows among retail investors and institutions alike,
scalability solutions such as Taproot upgrades,Lightning Network implementations,and sidechains aim to facilitate faster processing at lower costs.
These technological advancements could help sustain higher throughput levels necessary for mainstream adoption while reducing congestion-related fee hikes seen earlier this year.
Moreover,
wider acceptance from merchants accepting bitcoin payments directly enhances real-world utility beyond speculative trading,
potentially leading toward sustained growth in total number of daily transactions over coming years.
By continuously monitoring metrics like total bitcoin transaction count alongside technological improvements and regulatory changes,
stakeholders—from individual users to large-scale investors—can better understand market dynamics
and make informed decisions aligned with evolving industry conditions.
References
- CoinDesk — General information on Bitcoin networks
- Blockchain.com Charts — Historical data analysis
- Blockchain Size Data — Blockchain growth insights
- Transaction Fees & Congestion — Impact analysis
- Bitcoin Mining Process — Technical validation overview
- Regulatory Impact Reports — Policy effects assessment
Understanding how many people transact using Bitcoin provides valuable insight into its current state—and future potential—as both an investment asset and a decentralized payment system amidst an ever-changing global landscape
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What is Wallet Address Clustering?
Wallet address clustering is a crucial technique in the blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystem that involves grouping multiple wallet addresses based on shared transaction behaviors or characteristics. This process helps analysts, security professionals, and regulators better understand how digital assets move across the network, identify potential illicit activities, and improve privacy measures for users.
Understanding Wallet Addresses in Cryptocurrency
In the world of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, each user interacts with the blockchain through wallet addresses—unique alphanumeric strings that serve as digital bank accounts. These addresses are generated cryptographically to ensure pseudonymity; they do not directly reveal personal identities. However, despite this pseudonymity, all transactions linked to these addresses are publicly recorded on the blockchain ledger.
As transaction volumes grow exponentially over time, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain complete anonymity for individual users. Every transaction leaves a trail that can potentially be traced back to specific entities or behaviors if analyzed correctly. This is where wallet address clustering comes into play—it aims to analyze patterns across multiple addresses to infer relationships or groupings.
How Does Wallet Address Clustering Work?
Wallet address clustering employs various algorithms and analytical techniques designed to detect similarities among different addresses based on their activity patterns. These methods include:
- Transaction Pattern Analysis: Examining transfer amounts, timing between transactions, and frequency.
- Behavioral Signatures: Identifying common usage habits such as recurring transfers or specific asset types.
- Graph-Based Clustering: Creating visual maps of interconnected addresses based on shared inputs or outputs within transactions.
Popular algorithms used in this context include k-means clustering (which partitions data into predefined groups), hierarchical clustering (which builds nested clusters), and density-based methods like DBSCAN (which identifies clusters of varying shapes). Each has its strengths depending on dataset complexity and analysis goals.
Why Is Wallet Address Clustering Important?
The significance of wallet address clustering extends across several key areas:
Enhancing Privacy
While cryptocurrencies are often touted for their privacy features, true anonymity remains elusive due to transparent transaction records. By grouping related addresses together through clustering techniques, third parties find it more challenging to link individual transactions back to specific users—especially when combined with other privacy-preserving tools like mixers or privacy coins.
Security Monitoring
Clustering enables security teams and law enforcement agencies to detect suspicious activities such as money laundering schemes or fraud rings by spotting unusual patterns—like rapid transfers between clustered groups or large volume spikes—that deviate from typical user behavior.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions operating within regulatory frameworks use wallet address analysis for anti-money laundering (AML) efforts and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures. While full anonymization isn't always possible with effective clustering tools, these techniques help create a more compliant environment by providing insights into transactional relationships without exposing sensitive details unnecessarily.
Recent Advances in Wallet Address Clustering
Over recent years, significant progress has been made in refining clustering methodologies:
- Improved Algorithms: Researchers have developed sophisticated models capable of handling vast datasets efficiently while uncovering complex behavioral patterns.
- Integration Into Blockchain Analytics Platforms: Major analytics providers now incorporate advanced clustering features into their tools—enabling users ranging from law enforcement agencies to financial firms—to gain deeper insights.
- Privacy-Centric Cryptocurrencies: Some projects have integrated cluster-aware features directly into their protocols—for example, enhancing user privacy while still allowing legitimate analysis under certain conditions—which reflects ongoing innovation balancing transparency with confidentiality.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, wallet address clustering raises important concerns:
Regulatory Dilemmas: As authorities seek greater oversight over illicit activities like money laundering or terrorist financing via blockchain analysis tools—including those employing clustering—they face challenges balancing user privacy rights against compliance needs.
Potential for Misuse: If improperly implemented—or used without proper safeguards—clustering could inadvertently obscure legitimate transactions involving businesses or individuals who rely on enhanced privacy measures.
Ethical Debates: The debate continues around whether such analytical techniques should be solely used for security purposes—or if they risk infringing upon personal freedoms by enabling pervasive surveillance without adequate oversight.
Timeline of Key Developments
Understanding how wallet address clustering has evolved provides context about its current state:
- 2020: Academic research focused on evaluating different algorithms' effectiveness at preserving user privacy while enabling meaningful analysis.
- 2021: Major blockchain analytics platforms began integrating advanced cluster detection features amid rising demand from compliance-focused clients.
- 2022: The rise of privacy-centric cryptocurrencies prompted developers to embed cluster-aware mechanisms directly within protocols themselves.
- 2023: Regulatory discussions intensified regarding how best practices can balance effective AML/KYC processes with respecting individual rights—a debate ongoing today.
By grasping what wallet address clustering entails—and recognizing both its capabilities and limitations—you can better appreciate its role within broader efforts toward secure yet private cryptocurrency usage. Whether you're an investor seeking insight into transaction behaviors—or a regulator aiming at compliance—the evolving landscape underscores the importance of understanding this powerful analytical tool in today's digital economy.
Keywords: cryptocurrency wallets | blockchain analysis | transaction pattern recognition | crypto privacy | AML compliance | crypto security | decentralized finance


Lo
2025-05-15 03:19
What is wallet address clustering?
What is Wallet Address Clustering?
Wallet address clustering is a crucial technique in the blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystem that involves grouping multiple wallet addresses based on shared transaction behaviors or characteristics. This process helps analysts, security professionals, and regulators better understand how digital assets move across the network, identify potential illicit activities, and improve privacy measures for users.
Understanding Wallet Addresses in Cryptocurrency
In the world of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, each user interacts with the blockchain through wallet addresses—unique alphanumeric strings that serve as digital bank accounts. These addresses are generated cryptographically to ensure pseudonymity; they do not directly reveal personal identities. However, despite this pseudonymity, all transactions linked to these addresses are publicly recorded on the blockchain ledger.
As transaction volumes grow exponentially over time, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain complete anonymity for individual users. Every transaction leaves a trail that can potentially be traced back to specific entities or behaviors if analyzed correctly. This is where wallet address clustering comes into play—it aims to analyze patterns across multiple addresses to infer relationships or groupings.
How Does Wallet Address Clustering Work?
Wallet address clustering employs various algorithms and analytical techniques designed to detect similarities among different addresses based on their activity patterns. These methods include:
- Transaction Pattern Analysis: Examining transfer amounts, timing between transactions, and frequency.
- Behavioral Signatures: Identifying common usage habits such as recurring transfers or specific asset types.
- Graph-Based Clustering: Creating visual maps of interconnected addresses based on shared inputs or outputs within transactions.
Popular algorithms used in this context include k-means clustering (which partitions data into predefined groups), hierarchical clustering (which builds nested clusters), and density-based methods like DBSCAN (which identifies clusters of varying shapes). Each has its strengths depending on dataset complexity and analysis goals.
Why Is Wallet Address Clustering Important?
The significance of wallet address clustering extends across several key areas:
Enhancing Privacy
While cryptocurrencies are often touted for their privacy features, true anonymity remains elusive due to transparent transaction records. By grouping related addresses together through clustering techniques, third parties find it more challenging to link individual transactions back to specific users—especially when combined with other privacy-preserving tools like mixers or privacy coins.
Security Monitoring
Clustering enables security teams and law enforcement agencies to detect suspicious activities such as money laundering schemes or fraud rings by spotting unusual patterns—like rapid transfers between clustered groups or large volume spikes—that deviate from typical user behavior.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions operating within regulatory frameworks use wallet address analysis for anti-money laundering (AML) efforts and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures. While full anonymization isn't always possible with effective clustering tools, these techniques help create a more compliant environment by providing insights into transactional relationships without exposing sensitive details unnecessarily.
Recent Advances in Wallet Address Clustering
Over recent years, significant progress has been made in refining clustering methodologies:
- Improved Algorithms: Researchers have developed sophisticated models capable of handling vast datasets efficiently while uncovering complex behavioral patterns.
- Integration Into Blockchain Analytics Platforms: Major analytics providers now incorporate advanced clustering features into their tools—enabling users ranging from law enforcement agencies to financial firms—to gain deeper insights.
- Privacy-Centric Cryptocurrencies: Some projects have integrated cluster-aware features directly into their protocols—for example, enhancing user privacy while still allowing legitimate analysis under certain conditions—which reflects ongoing innovation balancing transparency with confidentiality.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, wallet address clustering raises important concerns:
Regulatory Dilemmas: As authorities seek greater oversight over illicit activities like money laundering or terrorist financing via blockchain analysis tools—including those employing clustering—they face challenges balancing user privacy rights against compliance needs.
Potential for Misuse: If improperly implemented—or used without proper safeguards—clustering could inadvertently obscure legitimate transactions involving businesses or individuals who rely on enhanced privacy measures.
Ethical Debates: The debate continues around whether such analytical techniques should be solely used for security purposes—or if they risk infringing upon personal freedoms by enabling pervasive surveillance without adequate oversight.
Timeline of Key Developments
Understanding how wallet address clustering has evolved provides context about its current state:
- 2020: Academic research focused on evaluating different algorithms' effectiveness at preserving user privacy while enabling meaningful analysis.
- 2021: Major blockchain analytics platforms began integrating advanced cluster detection features amid rising demand from compliance-focused clients.
- 2022: The rise of privacy-centric cryptocurrencies prompted developers to embed cluster-aware mechanisms directly within protocols themselves.
- 2023: Regulatory discussions intensified regarding how best practices can balance effective AML/KYC processes with respecting individual rights—a debate ongoing today.
By grasping what wallet address clustering entails—and recognizing both its capabilities and limitations—you can better appreciate its role within broader efforts toward secure yet private cryptocurrency usage. Whether you're an investor seeking insight into transaction behaviors—or a regulator aiming at compliance—the evolving landscape underscores the importance of understanding this powerful analytical tool in today's digital economy.
Keywords: cryptocurrency wallets | blockchain analysis | transaction pattern recognition | crypto privacy | AML compliance | crypto security | decentralized finance
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What Is Blockchain Interoperability? A Complete Overview
Understanding Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and transfer assets seamlessly. Unlike traditional financial systems where institutions can easily exchange information through standardized protocols, blockchain ecosystems are often isolated due to differing architectures and protocols. Interoperability aims to bridge these gaps, creating a more interconnected decentralized environment. This capability is essential for enabling cross-chain transactions, expanding the utility of digital assets, and fostering innovation across various blockchain platforms.
Why Is Interoperability Important in Blockchain Technology?
As blockchain technology matures, its applications have diversified into areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), supply chain management, and more. These use cases often require interaction between multiple blockchains—for example, transferring an NFT from one platform to another or executing a DeFi trade across different networks. Without interoperability, users face fragmentation; they must navigate multiple interfaces or convert assets manually through exchanges.
Interoperability enhances user experience by allowing smooth asset transfers and data sharing without intermediaries or complex procedures. It also promotes scalability by enabling specialized blockchains optimized for specific tasks while still maintaining connectivity with broader ecosystems.
Types of Blockchain Interoperability
There are primarily two types of interoperability based on how blockchains connect:
Homogeneous Interoperability: This involves different chains that share similar consensus mechanisms and protocols—think of it as connecting similar "languages." For example, two Ethereum-compatible chains can communicate more straightforwardly because they follow compatible standards.
Heterogeneous Interoperability: This connects fundamentally different blockchains with distinct architectures—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum—requiring more complex solutions like cross-chain bridges or protocol adapters.
Technologies Enabling Cross-Chain Communication
Several innovative technologies facilitate interoperability:
Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps: These enable the direct exchange of assets between two separate blockchains without intermediaries. They rely on smart contracts that ensure both parties fulfill their obligations simultaneously.
Sidechains: Smaller chains linked to a main chain via pegging mechanisms allow assets to move back and forth securely while leveraging the main chain’s security features.
Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like Lightning Network (Bitcoin) or Optimism (Ethereum) improve scalability and enable faster cross-chain interactions by processing transactions off the main chain before settling them on-chain.
Interoperability Protocols:
- Cosmos IBC: The Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol allows independent zones within Cosmos’ ecosystem—and beyond—to transfer data securely.
- Polkadot Relay Chain: Acts as a central hub connecting various parachains (independent but connected chains), facilitating asset transfers across diverse networks.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Interoperability
Despite promising advancements, several hurdles remain:
Scalability Concerns: Ensuring rapid transaction speeds without compromising security is challenging when connecting multiple networks with varying capacities.
Security Risks: Cross-chain bridges are vulnerable points; exploits could lead to significant losses if not properly secured against attacks such as double-spending or 51% attacks.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Different jurisdictions impose varying rules on cryptocurrencies which complicate compliance efforts during cross-border transactions involving multiple legal frameworks.
Recent Developments in Cross-Chain Compatibility
The landscape has seen notable progress recently:
Cosmos launched its IBC protocol in 2020, enabling seamless communication among Cosmos-based chains—a significant step toward an interconnected ecosystem.
Polkadot’s Relay Chain has been operational since 2020; it facilitates asset transfers between parachains within its network while exploring connections outside its ecosystem.
Binance Smart Chain has integrated several interoperability solutions including atomic swaps and sidechain integrations with Ethereum-compatible projects.
Solana is actively exploring partnerships aimed at bridging its high-performance network with Ethereum through technological collaborations designed for cross-platform compatibility.
Potential Risks & Future Outlook
While these developments mark substantial progress toward interconnectedness in blockchain space, potential risks could impact adoption:
Security vulnerabilities remain a concern if bridges aren’t implemented correctly—they could be exploited leading to loss of funds or data breaches.
Regulatory challenges may arise as authorities develop frameworks around cross-border digital asset movements; inconsistent policies might hinder seamless integration globally.
Market sentiment can also be affected by technological failures or delays in deploying robust interoperability solutions—affecting investor confidence and asset prices alike.
Looking ahead,
the push towards universal compatibility continues driven by demand from users seeking streamlined experiences across platforms. As technical standards mature alongside regulatory clarity,
blockchain interoperability promises not only enhanced functionality but also increased mainstream adoption of decentralized technologies.
Understanding how diverse networks connect will be vital for developers aiming at building scalable dApps,
investors seeking diversified portfolios,
and regulators working towards balanced oversight that fosters innovation without compromising security.
By addressing current challenges head-on through collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders,
the vision of an fully interoperable blockchain universe becomes increasingly attainable—one where digital assets flow freely regardless of underlying architecture.
This comprehensive overview underscores why blockchain interoperability is fundamental for advancing decentralized technology's potential—and why ongoing innovations will shape the future landscape significantly


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-15 03:34
What is interoperability between blockchains?
What Is Blockchain Interoperability? A Complete Overview
Understanding Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and transfer assets seamlessly. Unlike traditional financial systems where institutions can easily exchange information through standardized protocols, blockchain ecosystems are often isolated due to differing architectures and protocols. Interoperability aims to bridge these gaps, creating a more interconnected decentralized environment. This capability is essential for enabling cross-chain transactions, expanding the utility of digital assets, and fostering innovation across various blockchain platforms.
Why Is Interoperability Important in Blockchain Technology?
As blockchain technology matures, its applications have diversified into areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), supply chain management, and more. These use cases often require interaction between multiple blockchains—for example, transferring an NFT from one platform to another or executing a DeFi trade across different networks. Without interoperability, users face fragmentation; they must navigate multiple interfaces or convert assets manually through exchanges.
Interoperability enhances user experience by allowing smooth asset transfers and data sharing without intermediaries or complex procedures. It also promotes scalability by enabling specialized blockchains optimized for specific tasks while still maintaining connectivity with broader ecosystems.
Types of Blockchain Interoperability
There are primarily two types of interoperability based on how blockchains connect:
Homogeneous Interoperability: This involves different chains that share similar consensus mechanisms and protocols—think of it as connecting similar "languages." For example, two Ethereum-compatible chains can communicate more straightforwardly because they follow compatible standards.
Heterogeneous Interoperability: This connects fundamentally different blockchains with distinct architectures—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum—requiring more complex solutions like cross-chain bridges or protocol adapters.
Technologies Enabling Cross-Chain Communication
Several innovative technologies facilitate interoperability:
Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps: These enable the direct exchange of assets between two separate blockchains without intermediaries. They rely on smart contracts that ensure both parties fulfill their obligations simultaneously.
Sidechains: Smaller chains linked to a main chain via pegging mechanisms allow assets to move back and forth securely while leveraging the main chain’s security features.
Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like Lightning Network (Bitcoin) or Optimism (Ethereum) improve scalability and enable faster cross-chain interactions by processing transactions off the main chain before settling them on-chain.
Interoperability Protocols:
- Cosmos IBC: The Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol allows independent zones within Cosmos’ ecosystem—and beyond—to transfer data securely.
- Polkadot Relay Chain: Acts as a central hub connecting various parachains (independent but connected chains), facilitating asset transfers across diverse networks.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Interoperability
Despite promising advancements, several hurdles remain:
Scalability Concerns: Ensuring rapid transaction speeds without compromising security is challenging when connecting multiple networks with varying capacities.
Security Risks: Cross-chain bridges are vulnerable points; exploits could lead to significant losses if not properly secured against attacks such as double-spending or 51% attacks.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Different jurisdictions impose varying rules on cryptocurrencies which complicate compliance efforts during cross-border transactions involving multiple legal frameworks.
Recent Developments in Cross-Chain Compatibility
The landscape has seen notable progress recently:
Cosmos launched its IBC protocol in 2020, enabling seamless communication among Cosmos-based chains—a significant step toward an interconnected ecosystem.
Polkadot’s Relay Chain has been operational since 2020; it facilitates asset transfers between parachains within its network while exploring connections outside its ecosystem.
Binance Smart Chain has integrated several interoperability solutions including atomic swaps and sidechain integrations with Ethereum-compatible projects.
Solana is actively exploring partnerships aimed at bridging its high-performance network with Ethereum through technological collaborations designed for cross-platform compatibility.
Potential Risks & Future Outlook
While these developments mark substantial progress toward interconnectedness in blockchain space, potential risks could impact adoption:
Security vulnerabilities remain a concern if bridges aren’t implemented correctly—they could be exploited leading to loss of funds or data breaches.
Regulatory challenges may arise as authorities develop frameworks around cross-border digital asset movements; inconsistent policies might hinder seamless integration globally.
Market sentiment can also be affected by technological failures or delays in deploying robust interoperability solutions—affecting investor confidence and asset prices alike.
Looking ahead,
the push towards universal compatibility continues driven by demand from users seeking streamlined experiences across platforms. As technical standards mature alongside regulatory clarity,
blockchain interoperability promises not only enhanced functionality but also increased mainstream adoption of decentralized technologies.
Understanding how diverse networks connect will be vital for developers aiming at building scalable dApps,
investors seeking diversified portfolios,
and regulators working towards balanced oversight that fosters innovation without compromising security.
By addressing current challenges head-on through collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders,
the vision of an fully interoperable blockchain universe becomes increasingly attainable—one where digital assets flow freely regardless of underlying architecture.
This comprehensive overview underscores why blockchain interoperability is fundamental for advancing decentralized technology's potential—and why ongoing innovations will shape the future landscape significantly
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What Are Blockchain Analytics Tools?
Blockchain analytics tools are software platforms designed to analyze and interpret data from blockchain networks. These tools help users track transactions, monitor network activity, assess market trends, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. As blockchain technology becomes more widespread, the need for transparent and reliable analytics has grown exponentially. Whether you're an investor, regulator, or developer, understanding how these tools work is essential for navigating the complex landscape of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi).
These platforms leverage advanced algorithms to sift through vast amounts of on-chain data—such as transaction histories, wallet addresses, token movements—and present insights in a user-friendly manner. They also incorporate features like risk assessment and compliance checks to help institutions meet legal requirements while maintaining transparency.
Leading Blockchain Analytics Platforms
Several key players dominate the blockchain analytics space today. Each offers unique features tailored to different needs within the ecosystem:
Chainalysis
Chainalysis stands out as one of the most comprehensive solutions available for blockchain analysis. It provides real-time transaction monitoring that helps identify suspicious activities such as money laundering or fraud attempts. Its detailed reports on cryptocurrency flows assist law enforcement agencies and financial institutions in tracking illicit transactions across multiple blockchains.
In 2023, Chainalysis introduced "CryptoSlate," a feature that delivers deeper insights into market performance trends—making it easier for users to understand broader industry shifts alongside individual transaction data.
Elliptic
Elliptic specializes in anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance solutions tailored for financial institutions operating within crypto markets. Its platform offers advanced risk scoring models based on transaction patterns and wallet behaviors.
Recent updates in 2024 expanded Elliptic’s coverage to include more cryptocurrencies beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum—covering emerging tokens used in DeFi applications—and broadened its client base among banks and exchanges seeking regulatory adherence.
Glassnode
Unlike traditional analytics focusing solely on transactional data, Glassnode emphasizes on-chain metrics that gauge network health and market sentiment. Metrics like Network Value to Transactions (NVT) ratio or Market Value to Realized Value (MVRV) provide insights into whether a cryptocurrency is overbought or undervalued.
In 2025, Glassnode launched new analytical ratios such as "NVT Ratio" which helps traders assess whether current prices reflect underlying network activity—a vital tool during periods of high volatility when quick decision-making is crucial.
CryptoSlate
CryptoSlate acts as an aggregator platform pulling data from various sources—including other analytics tools—to offer comprehensive reports about crypto markets globally. It combines real-time price feeds with news updates relevant to ongoing developments within blockchain ecosystems.
The platform's recent expansion in 2024 included enhanced NFT tracking features—allowing users not only to monitor token sales but also analyze buying patterns across digital art marketplaces—a reflection of NFT market maturation.
Nansen
Nansen focuses heavily on decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Its strength lies in providing granular insights into user behavior—such as large wallet movements or protocol-specific risk factors—which are invaluable for investors looking at yield farming strategies or NFT investments.
In 2025, Nansen partnered with major DeFi projects aiming at improving its risk assessment capabilities further—helping users avoid scams while optimizing their investment strategies based on behavioral signals observed across protocols.
Recent Trends Shaping Blockchain Analytics Tools
The development of these platforms has been influenced by several recent industry trends:
Regulatory Environment: Governments worldwide have increased scrutiny over crypto activities since 2023. Tools like Chainalysis have played pivotal roles by helping exchanges comply with AML/KYC regulations through detailed transaction monitoring.
Market Volatility: The unpredictable swings seen recently make real-time analysis more critical than ever; platforms like Glassnode provide timely metrics that inform trading decisions during turbulent periods.
Growth of DeFi: Decentralized finance continues expanding rapidly; Nansen’s focus on DeFi protocols allows investors to navigate this complex sector effectively.
NFT Market Expansion: The surge in digital collectibles has prompted analytic providers like CryptoSlate to develop specialized modules tracking NFT sales volumes & buyer behaviors.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Analytics Solutions
Despite their advantages, these tools face several hurdles:
Regulatory Risks: As authorities impose stricter rules around privacy & transparency standards—for example GDPR-like regulations—they may limit what data can be collected & analyzed legally.
Data Privacy Concerns: Large-scale collection raises questions about user privacy rights; balancing transparency with confidentiality remains a delicate issue.
Market Fluctuations Impact Accuracy: Rapid price swings can distort metrics temporarily; analytic models must adapt quickly without producing misleading signals.
Intense Competition & Innovation Pressure: With many startups entering this space regularly—from niche providers focusing solely on NFTs or specific chains—the landscape demands continuous innovation.
Why Blockchain Analytics Matter Today
Understanding how these tools function is crucial not just for traders but also regulators seeking transparency within increasingly complex networks. They enable detection of illicit activities such as frauds or money laundering while supporting compliance efforts globally—a vital aspect considering evolving legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies worldwide.
Moreover, they empower investors by providing actionable insights derived from deep analysis rather than speculation alone — especially important amid volatile markets where timing can significantly impact profitability.
Future Outlook: Evolving Capabilities & Industry Needs
As blockchain technology matures further—with innovations like layer-two scaling solutions—the role of analytics will become even more significant. Future developments may include enhanced AI-driven predictive models capable of forecasting market movements before they happen or improved cross-chain analysis enabling seamless tracking across multiple networks simultaneously.
Furthermore:
- Increased integration between different analytical platforms could foster richer datasets.*
- Privacy-preserving techniques might emerge allowing detailed analysis without compromising user confidentiality.*
- Regulatory frameworks will likely shape product offerings further—as companies adapt their services accordingly.*
Staying informed about these advancements ensures stakeholders remain equipped with cutting-edge tools necessary for navigating this dynamic environment effectively.
Keywords: blockchain analytics tools , cryptocurrency monitoring software , DeFi analysis platforms , NFT trend trackers , AML/KYC solutions , real-time transaction monitoring


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 08:49
What tools exist for blockchain analytics?
What Are Blockchain Analytics Tools?
Blockchain analytics tools are software platforms designed to analyze and interpret data from blockchain networks. These tools help users track transactions, monitor network activity, assess market trends, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. As blockchain technology becomes more widespread, the need for transparent and reliable analytics has grown exponentially. Whether you're an investor, regulator, or developer, understanding how these tools work is essential for navigating the complex landscape of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi).
These platforms leverage advanced algorithms to sift through vast amounts of on-chain data—such as transaction histories, wallet addresses, token movements—and present insights in a user-friendly manner. They also incorporate features like risk assessment and compliance checks to help institutions meet legal requirements while maintaining transparency.
Leading Blockchain Analytics Platforms
Several key players dominate the blockchain analytics space today. Each offers unique features tailored to different needs within the ecosystem:
Chainalysis
Chainalysis stands out as one of the most comprehensive solutions available for blockchain analysis. It provides real-time transaction monitoring that helps identify suspicious activities such as money laundering or fraud attempts. Its detailed reports on cryptocurrency flows assist law enforcement agencies and financial institutions in tracking illicit transactions across multiple blockchains.
In 2023, Chainalysis introduced "CryptoSlate," a feature that delivers deeper insights into market performance trends—making it easier for users to understand broader industry shifts alongside individual transaction data.
Elliptic
Elliptic specializes in anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance solutions tailored for financial institutions operating within crypto markets. Its platform offers advanced risk scoring models based on transaction patterns and wallet behaviors.
Recent updates in 2024 expanded Elliptic’s coverage to include more cryptocurrencies beyond Bitcoin and Ethereum—covering emerging tokens used in DeFi applications—and broadened its client base among banks and exchanges seeking regulatory adherence.
Glassnode
Unlike traditional analytics focusing solely on transactional data, Glassnode emphasizes on-chain metrics that gauge network health and market sentiment. Metrics like Network Value to Transactions (NVT) ratio or Market Value to Realized Value (MVRV) provide insights into whether a cryptocurrency is overbought or undervalued.
In 2025, Glassnode launched new analytical ratios such as "NVT Ratio" which helps traders assess whether current prices reflect underlying network activity—a vital tool during periods of high volatility when quick decision-making is crucial.
CryptoSlate
CryptoSlate acts as an aggregator platform pulling data from various sources—including other analytics tools—to offer comprehensive reports about crypto markets globally. It combines real-time price feeds with news updates relevant to ongoing developments within blockchain ecosystems.
The platform's recent expansion in 2024 included enhanced NFT tracking features—allowing users not only to monitor token sales but also analyze buying patterns across digital art marketplaces—a reflection of NFT market maturation.
Nansen
Nansen focuses heavily on decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Its strength lies in providing granular insights into user behavior—such as large wallet movements or protocol-specific risk factors—which are invaluable for investors looking at yield farming strategies or NFT investments.
In 2025, Nansen partnered with major DeFi projects aiming at improving its risk assessment capabilities further—helping users avoid scams while optimizing their investment strategies based on behavioral signals observed across protocols.
Recent Trends Shaping Blockchain Analytics Tools
The development of these platforms has been influenced by several recent industry trends:
Regulatory Environment: Governments worldwide have increased scrutiny over crypto activities since 2023. Tools like Chainalysis have played pivotal roles by helping exchanges comply with AML/KYC regulations through detailed transaction monitoring.
Market Volatility: The unpredictable swings seen recently make real-time analysis more critical than ever; platforms like Glassnode provide timely metrics that inform trading decisions during turbulent periods.
Growth of DeFi: Decentralized finance continues expanding rapidly; Nansen’s focus on DeFi protocols allows investors to navigate this complex sector effectively.
NFT Market Expansion: The surge in digital collectibles has prompted analytic providers like CryptoSlate to develop specialized modules tracking NFT sales volumes & buyer behaviors.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Analytics Solutions
Despite their advantages, these tools face several hurdles:
Regulatory Risks: As authorities impose stricter rules around privacy & transparency standards—for example GDPR-like regulations—they may limit what data can be collected & analyzed legally.
Data Privacy Concerns: Large-scale collection raises questions about user privacy rights; balancing transparency with confidentiality remains a delicate issue.
Market Fluctuations Impact Accuracy: Rapid price swings can distort metrics temporarily; analytic models must adapt quickly without producing misleading signals.
Intense Competition & Innovation Pressure: With many startups entering this space regularly—from niche providers focusing solely on NFTs or specific chains—the landscape demands continuous innovation.
Why Blockchain Analytics Matter Today
Understanding how these tools function is crucial not just for traders but also regulators seeking transparency within increasingly complex networks. They enable detection of illicit activities such as frauds or money laundering while supporting compliance efforts globally—a vital aspect considering evolving legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies worldwide.
Moreover, they empower investors by providing actionable insights derived from deep analysis rather than speculation alone — especially important amid volatile markets where timing can significantly impact profitability.
Future Outlook: Evolving Capabilities & Industry Needs
As blockchain technology matures further—with innovations like layer-two scaling solutions—the role of analytics will become even more significant. Future developments may include enhanced AI-driven predictive models capable of forecasting market movements before they happen or improved cross-chain analysis enabling seamless tracking across multiple networks simultaneously.
Furthermore:
- Increased integration between different analytical platforms could foster richer datasets.*
- Privacy-preserving techniques might emerge allowing detailed analysis without compromising user confidentiality.*
- Regulatory frameworks will likely shape product offerings further—as companies adapt their services accordingly.*
Staying informed about these advancements ensures stakeholders remain equipped with cutting-edge tools necessary for navigating this dynamic environment effectively.
Keywords: blockchain analytics tools , cryptocurrency monitoring software , DeFi analysis platforms , NFT trend trackers , AML/KYC solutions , real-time transaction monitoring
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What Is a Private Key in Cryptocurrency?
A private key is a fundamental element in the world of blockchain and digital currencies. Think of it as a secret password or digital signature that grants access to your cryptocurrency holdings. Unlike your public address, which you can share openly to receive funds, your private key must remain confidential because it provides control over your assets. If someone gains access to your private key, they can potentially transfer or spend all associated funds without your permission.
In essence, the private key is what authorizes transactions on blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It’s generated through cryptographic algorithms that ensure its uniqueness and security. The strength of this system relies heavily on keeping this key secret; otherwise, the security of your digital assets could be compromised.
How Does a Private Key Work in Blockchain Transactions?
Understanding how private keys function within blockchain transactions involves several steps:
1. Generating a Key Pair
When you create a cryptocurrency wallet, it automatically generates two cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. The public key acts as an address where others can send you funds—think of it as an email address for receiving money—while the private key remains secret with you.
2. Signing Transactions
To send cryptocurrencies from your wallet, you need to sign the transaction using your private key. This process creates a unique digital signature that proves ownership without revealing the actual private key itself.
3. Verification by Network Nodes
Once signed, the transaction is broadcasted across the network (like Bitcoin or Ethereum). Network nodes verify that the signature matches with the sender’s public key—confirming authenticity—and then add it to the blockchain ledger if valid.
This cryptographic process ensures both security and integrity: only someone with access to the correct private key can authorize spending from an account, preventing unauthorized transactions.
Why Are Private Keys Critical for Digital Asset Security?
Private keys are at the core of securing digital assets because they provide proof of ownership and authorization rights within decentralized systems:
- Confidentiality: Since anyone with access to this secret code can control associated funds, safeguarding it is paramount.
- Irreversibility: Unlike traditional banking systems where errors might be rectified easily, losing access to your private keys typically means losing all control over those assets permanently.
- Security Risks: If exposed through hacking attempts like phishing or malware attacks, malicious actors could drain accounts instantly.
Because these risks are so significant, users often employ various methods such as hardware wallets or encrypted backups to protect their keys effectively.
Types of Private Keys Used in Cryptocurrency Wallets
There are different formats for storing and managing private keys depending on user needs:
- Hexadecimal Strings: Long strings composed solely of numbers 0–9 and letters A–F.
- Wallet Files (e.g., .json files): Encrypted files containing encrypted versions of keys used by software wallets.
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices like Ledger Nano S/X or Trezor store private keys offline for enhanced security.
Each method offers varying levels of convenience versus security; hardware wallets are generally considered most secure against online threats because they keep keys isolated from internet-connected devices.
Recent Developments in Private Key Management
The landscape around managing crypto-private keys continues evolving rapidly due to technological advancements:
Hardware Wallets Advancements
Devices such as Ledger Nano X have improved user experience while maintaining high-security standards by storing sensitive data offline—a practice known as cold storage—which significantly reduces hacking risks.
Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature (multi-sig) setups require multiple independent signatures before executing transactions—adding layers of approval that prevent single points-of-failure or theft if one device gets compromised.
Quantum Computing Concerns
Emerging quantum computing technology poses potential threats since current cryptography may become vulnerable under powerful quantum algorithms. Researchers are actively developing post-quantum cryptography solutions designed specifically for resisting such attacks without compromising performance today’s systems rely upon.
Regulatory Focus & Industry Standards
As governments worldwide implement regulations around cryptocurrencies’ custody practices—including how users should securely manage their private keys—the industry sees increased adoption of standardized protocols emphasizing secure storage solutions like hardware wallets combined with best practices for backup procedures.
Risks Associated With Private Keys
Despite their importance in securing digital assets, mishandling or exposure poses serious dangers:
Loss Due To Forgetfulness or Damage: Losing physical copies (like paper backups) means permanent loss unless properly stored elsewhere.
Theft Through Phishing & Malware Attacks: Attackers often trick users into revealing their secrets via fake websites (“phishing”) or infecting devices with malware designed specifically for stealing keystrokes or clipboard data containing sensitive information.
Regulatory Non-compliance Risks: Failing to follow proper management procedures may lead not only to financial loss but also legal consequences depending on jurisdictional requirements.
Best Practices For Managing Your Private Keys Safely
To minimize risks associated with handling crypto-private keys:
- Use hardware wallets whenever possible—they store secrets offline away from internet vulnerabilities.
- Create multiple encrypted backups stored securely in geographically separated locations.
- Never share/private reveal your seed phrases — avoid storing them digitally unless encrypted properly.
- Be cautious about phishing attempts; always verify URLs before entering sensitive information online.
- Keep software wallets updated regularly along with device firmware patches.
Staying informed about developments related to privacy-enhancing tools like multi-sig arrangements and advances against emerging threats such as quantum computing will help safeguard investments long-term while complying with evolving regulatory landscapes.
By understanding what exactly constitutes a private key—and adopting robust management strategies—you ensure better protection against thefts while maintaining full control over digital assets within decentralized ecosystems.
Keywords: cryptocurrency privacy tips | secure crypto storage | blockchain security best practices | managing crypto-privatekeys | multi-signature wallets | hardware wallet advantages


Lo
2025-05-06 08:02
What is a private key and how does it work?
What Is a Private Key in Cryptocurrency?
A private key is a fundamental element in the world of blockchain and digital currencies. Think of it as a secret password or digital signature that grants access to your cryptocurrency holdings. Unlike your public address, which you can share openly to receive funds, your private key must remain confidential because it provides control over your assets. If someone gains access to your private key, they can potentially transfer or spend all associated funds without your permission.
In essence, the private key is what authorizes transactions on blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It’s generated through cryptographic algorithms that ensure its uniqueness and security. The strength of this system relies heavily on keeping this key secret; otherwise, the security of your digital assets could be compromised.
How Does a Private Key Work in Blockchain Transactions?
Understanding how private keys function within blockchain transactions involves several steps:
1. Generating a Key Pair
When you create a cryptocurrency wallet, it automatically generates two cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. The public key acts as an address where others can send you funds—think of it as an email address for receiving money—while the private key remains secret with you.
2. Signing Transactions
To send cryptocurrencies from your wallet, you need to sign the transaction using your private key. This process creates a unique digital signature that proves ownership without revealing the actual private key itself.
3. Verification by Network Nodes
Once signed, the transaction is broadcasted across the network (like Bitcoin or Ethereum). Network nodes verify that the signature matches with the sender’s public key—confirming authenticity—and then add it to the blockchain ledger if valid.
This cryptographic process ensures both security and integrity: only someone with access to the correct private key can authorize spending from an account, preventing unauthorized transactions.
Why Are Private Keys Critical for Digital Asset Security?
Private keys are at the core of securing digital assets because they provide proof of ownership and authorization rights within decentralized systems:
- Confidentiality: Since anyone with access to this secret code can control associated funds, safeguarding it is paramount.
- Irreversibility: Unlike traditional banking systems where errors might be rectified easily, losing access to your private keys typically means losing all control over those assets permanently.
- Security Risks: If exposed through hacking attempts like phishing or malware attacks, malicious actors could drain accounts instantly.
Because these risks are so significant, users often employ various methods such as hardware wallets or encrypted backups to protect their keys effectively.
Types of Private Keys Used in Cryptocurrency Wallets
There are different formats for storing and managing private keys depending on user needs:
- Hexadecimal Strings: Long strings composed solely of numbers 0–9 and letters A–F.
- Wallet Files (e.g., .json files): Encrypted files containing encrypted versions of keys used by software wallets.
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices like Ledger Nano S/X or Trezor store private keys offline for enhanced security.
Each method offers varying levels of convenience versus security; hardware wallets are generally considered most secure against online threats because they keep keys isolated from internet-connected devices.
Recent Developments in Private Key Management
The landscape around managing crypto-private keys continues evolving rapidly due to technological advancements:
Hardware Wallets Advancements
Devices such as Ledger Nano X have improved user experience while maintaining high-security standards by storing sensitive data offline—a practice known as cold storage—which significantly reduces hacking risks.
Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature (multi-sig) setups require multiple independent signatures before executing transactions—adding layers of approval that prevent single points-of-failure or theft if one device gets compromised.
Quantum Computing Concerns
Emerging quantum computing technology poses potential threats since current cryptography may become vulnerable under powerful quantum algorithms. Researchers are actively developing post-quantum cryptography solutions designed specifically for resisting such attacks without compromising performance today’s systems rely upon.
Regulatory Focus & Industry Standards
As governments worldwide implement regulations around cryptocurrencies’ custody practices—including how users should securely manage their private keys—the industry sees increased adoption of standardized protocols emphasizing secure storage solutions like hardware wallets combined with best practices for backup procedures.
Risks Associated With Private Keys
Despite their importance in securing digital assets, mishandling or exposure poses serious dangers:
Loss Due To Forgetfulness or Damage: Losing physical copies (like paper backups) means permanent loss unless properly stored elsewhere.
Theft Through Phishing & Malware Attacks: Attackers often trick users into revealing their secrets via fake websites (“phishing”) or infecting devices with malware designed specifically for stealing keystrokes or clipboard data containing sensitive information.
Regulatory Non-compliance Risks: Failing to follow proper management procedures may lead not only to financial loss but also legal consequences depending on jurisdictional requirements.
Best Practices For Managing Your Private Keys Safely
To minimize risks associated with handling crypto-private keys:
- Use hardware wallets whenever possible—they store secrets offline away from internet vulnerabilities.
- Create multiple encrypted backups stored securely in geographically separated locations.
- Never share/private reveal your seed phrases — avoid storing them digitally unless encrypted properly.
- Be cautious about phishing attempts; always verify URLs before entering sensitive information online.
- Keep software wallets updated regularly along with device firmware patches.
Staying informed about developments related to privacy-enhancing tools like multi-sig arrangements and advances against emerging threats such as quantum computing will help safeguard investments long-term while complying with evolving regulatory landscapes.
By understanding what exactly constitutes a private key—and adopting robust management strategies—you ensure better protection against thefts while maintaining full control over digital assets within decentralized ecosystems.
Keywords: cryptocurrency privacy tips | secure crypto storage | blockchain security best practices | managing crypto-privatekeys | multi-signature wallets | hardware wallet advantages
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
$JU/USDT just hit new ATH: $22
Road to $50
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #JU

Mrconfamm
2025-08-30 17:54
$JU Touch new ATH
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
Understanding Proof-of-Stake (PoS) as a Blockchain Consensus Mechanism
Blockchain technology relies on consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the network. Among these, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) has gained significant attention as an energy-efficient alternative to traditional methods like Proof-of-Work (PoW). This article explores what PoS is, how it functions, its historical development, advantages, challenges, and recent trends shaping its future.
What Is Proof-of-Stake?
Proof-of-Stake is a consensus protocol that enables blockchain networks to agree on transaction validity without requiring extensive computational work. Unlike PoW systems—such as Bitcoin—that depend on miners solving complex mathematical puzzles using powerful hardware, PoS selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up in the network. This stake acts as collateral; if validators act maliciously or fail to perform their duties properly, they risk losing their staked tokens.
The core idea behind PoS is that those who have a vested interest in maintaining the network's security are more likely to act honestly. By tying validator incentives directly to their holdings, PoS aims to promote trustworthiness while significantly reducing energy consumption.
How Does Proof-of-Stake Work?
The process of validating transactions and creating new blocks in a PoS system involves several key steps:
Validator Selection
Validators are chosen based on their stake—the amount of cryptocurrency they have committed to the network. Generally speaking, larger stakes increase the probability of being selected for block creation because they represent a higher economic commitment. This proportional selection incentivizes validators to behave honestly since malicious actions could jeopardize their own assets.
Randomized Block Creation
Once selected through probabilistic algorithms—often involving random number generators—the validator proceeds with creating a new block containing recent transactions. To ensure fairness and prevent predictability or manipulation in validator selection, many systems incorporate additional randomness factors into this process.
Rewards and Penalties
Successful validation results in rewards such as newly minted coins and transaction fees added to the blockchain's ledger. Conversely, if validators attempt double-spending attacks or fail to produce blocks when selected—known as "missed" validations—they face penalties called "slashing." Slashing involves reducing or forfeiting part of their staked tokens as punishment for misconduct.
Security Measures: Slashing Penalties
Slashing serves both as an incentive for honest participation and a deterrent against malicious behavior like double-spending or equivocation (creating conflicting blocks). These penalties help uphold network security by aligning validator interests with overall system health.
The Evolution of Proof-of-Stake: A Brief History
While conceptually proposed back in 2012 by cryptographer Daniel Bernstein—a pioneer known for his contributions across cryptography—the first notable implementation appeared with Tezos in 2017. Tezos introduced innovative governance features allowing token holders themselves to vote on protocol upgrades—a model that enhanced community participation within proof-based consensus mechanisms.
Ethereum’s transition from proof-of-work toward hybrid proof-of-stake via Ethereum 2.0 has been pivotal for mainstream adoption. Launched initially through its Beacon Chain in December 2020—and ongoing since then—Ethereum aims at improving scalability while drastically reducing energy consumption associated with mining activities.
Other projects like Cardano utilize Ouroboros—a rigorous academic-designed PoS algorithm—to achieve secure decentralization from inception. Meanwhile, Solana combines elements from both PoS and other protocols such as Proof-of-History (PoH), enabling high throughput suitable for decentralized applications demanding fast transaction speeds.
Advantages of Using Proof-of-Stake
One primary benefit of PoS over traditional proof-based methods is its superior energy efficiency; validators do not need massive computational power but only hold tokens relevant enough relative stakes for participation rights. As such:
- Lower Energy Consumption: Since no intensive calculations are required.
- Enhanced Scalability: Faster validation times facilitate higher transaction throughput.
- Decentralization Potential: When designed inclusively—with low barriers for entry—it can foster broader participation among users globally.
Additionally, staking often encourages long-term engagement by rewarding token holders who commit assets over time rather than short-term miners seeking quick profits.
Challenges Facing Proof-of-Stake Networks
Despite its advantages, PoS faces certain risks:
Centralization Risks
Large stakeholders may accumulate disproportionate influence over decision-making processes within networks—potentially leading toward centralization where few entities control significant portions of staking power unless measures are implemented carefully during design phases.
Security Concerns
While generally considered secure when properly implemented—including slashing safeguards—PoS networks remain vulnerable under specific attack vectors such as “51% attacks,” where an entity controlling more than half the total stake could manipulate outcomes temporarily.
Furthermore, issues like “Nothing at Stake”—where validators might support multiple competing chains without penalty—have prompted developers worldwide to develop additional security patches and protocols addressing these vulnerabilities effectively over time.
Recent Trends & Future Outlook
The shift towards proof-based consensus models continues shaping blockchain ecosystems globally:
Ethereum’s Transition: The move towards Ethereum 2.0’s hybrid model aims at achieving greater scalability while maintaining decentralization standards—a complex but promising evolution expected over upcoming years.
Regulatory Scrutiny: As institutional interest grows around cryptocurrencies employing staking mechanisms—for example via DeFi platforms—regulators worldwide are examining legal frameworks surrounding staking activities which could impact future adoption strategies.
Security Improvements: Ongoing research into mitigating vulnerabilities like Nothing at Stake has led developers toward implementing multi-layered security measures ensuring robustness against potential exploits.
Community Engagement & Governance: Many projects leverage token-holder voting rights embedded within protocols encouraging active community involvement—which fosters transparency but also raises questions about influence concentration among large stakeholders.
Why Understanding Proof-of-Stake Matters
For investors considering cryptocurrencies utilizing PoS algorithms—or developers designing next-generation blockchain solutions—it’s crucial understanding both benefits and limitations inherent within this mechanism:
- Recognizing how validator incentives align with network health helps assess long-term sustainability prospects;
- Being aware of centralization risks guides better governance structures;
- Monitoring ongoing developments ensures preparedness amidst evolving regulatory landscapes;4.. Appreciating technical nuances supports informed decision-making regarding project viability or investment potential.
By grasping these core aspects rooted deeply in cryptographic principles—and supported by real-world implementations—you can better navigate today’s rapidly changing blockchain environment grounded increasingly upon proof-based consensus models like Proof-of-Stake.
This overview provides clarity around what makes proof-of-stake an influential component within modern blockchain architecture—from foundational concepts through current trends—all essential knowledge whether you're an investor aiming for informed decisions or developer seeking innovative solutions rooted in proven technology principles


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 04:42
Could you explain "Proof-of-Stake" (PoS) as a consensus mechanism?
Understanding Proof-of-Stake (PoS) as a Blockchain Consensus Mechanism
Blockchain technology relies on consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the network. Among these, Proof-of-Stake (PoS) has gained significant attention as an energy-efficient alternative to traditional methods like Proof-of-Work (PoW). This article explores what PoS is, how it functions, its historical development, advantages, challenges, and recent trends shaping its future.
What Is Proof-of-Stake?
Proof-of-Stake is a consensus protocol that enables blockchain networks to agree on transaction validity without requiring extensive computational work. Unlike PoW systems—such as Bitcoin—that depend on miners solving complex mathematical puzzles using powerful hardware, PoS selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up in the network. This stake acts as collateral; if validators act maliciously or fail to perform their duties properly, they risk losing their staked tokens.
The core idea behind PoS is that those who have a vested interest in maintaining the network's security are more likely to act honestly. By tying validator incentives directly to their holdings, PoS aims to promote trustworthiness while significantly reducing energy consumption.
How Does Proof-of-Stake Work?
The process of validating transactions and creating new blocks in a PoS system involves several key steps:
Validator Selection
Validators are chosen based on their stake—the amount of cryptocurrency they have committed to the network. Generally speaking, larger stakes increase the probability of being selected for block creation because they represent a higher economic commitment. This proportional selection incentivizes validators to behave honestly since malicious actions could jeopardize their own assets.
Randomized Block Creation
Once selected through probabilistic algorithms—often involving random number generators—the validator proceeds with creating a new block containing recent transactions. To ensure fairness and prevent predictability or manipulation in validator selection, many systems incorporate additional randomness factors into this process.
Rewards and Penalties
Successful validation results in rewards such as newly minted coins and transaction fees added to the blockchain's ledger. Conversely, if validators attempt double-spending attacks or fail to produce blocks when selected—known as "missed" validations—they face penalties called "slashing." Slashing involves reducing or forfeiting part of their staked tokens as punishment for misconduct.
Security Measures: Slashing Penalties
Slashing serves both as an incentive for honest participation and a deterrent against malicious behavior like double-spending or equivocation (creating conflicting blocks). These penalties help uphold network security by aligning validator interests with overall system health.
The Evolution of Proof-of-Stake: A Brief History
While conceptually proposed back in 2012 by cryptographer Daniel Bernstein—a pioneer known for his contributions across cryptography—the first notable implementation appeared with Tezos in 2017. Tezos introduced innovative governance features allowing token holders themselves to vote on protocol upgrades—a model that enhanced community participation within proof-based consensus mechanisms.
Ethereum’s transition from proof-of-work toward hybrid proof-of-stake via Ethereum 2.0 has been pivotal for mainstream adoption. Launched initially through its Beacon Chain in December 2020—and ongoing since then—Ethereum aims at improving scalability while drastically reducing energy consumption associated with mining activities.
Other projects like Cardano utilize Ouroboros—a rigorous academic-designed PoS algorithm—to achieve secure decentralization from inception. Meanwhile, Solana combines elements from both PoS and other protocols such as Proof-of-History (PoH), enabling high throughput suitable for decentralized applications demanding fast transaction speeds.
Advantages of Using Proof-of-Stake
One primary benefit of PoS over traditional proof-based methods is its superior energy efficiency; validators do not need massive computational power but only hold tokens relevant enough relative stakes for participation rights. As such:
- Lower Energy Consumption: Since no intensive calculations are required.
- Enhanced Scalability: Faster validation times facilitate higher transaction throughput.
- Decentralization Potential: When designed inclusively—with low barriers for entry—it can foster broader participation among users globally.
Additionally, staking often encourages long-term engagement by rewarding token holders who commit assets over time rather than short-term miners seeking quick profits.
Challenges Facing Proof-of-Stake Networks
Despite its advantages, PoS faces certain risks:
Centralization Risks
Large stakeholders may accumulate disproportionate influence over decision-making processes within networks—potentially leading toward centralization where few entities control significant portions of staking power unless measures are implemented carefully during design phases.
Security Concerns
While generally considered secure when properly implemented—including slashing safeguards—PoS networks remain vulnerable under specific attack vectors such as “51% attacks,” where an entity controlling more than half the total stake could manipulate outcomes temporarily.
Furthermore, issues like “Nothing at Stake”—where validators might support multiple competing chains without penalty—have prompted developers worldwide to develop additional security patches and protocols addressing these vulnerabilities effectively over time.
Recent Trends & Future Outlook
The shift towards proof-based consensus models continues shaping blockchain ecosystems globally:
Ethereum’s Transition: The move towards Ethereum 2.0’s hybrid model aims at achieving greater scalability while maintaining decentralization standards—a complex but promising evolution expected over upcoming years.
Regulatory Scrutiny: As institutional interest grows around cryptocurrencies employing staking mechanisms—for example via DeFi platforms—regulators worldwide are examining legal frameworks surrounding staking activities which could impact future adoption strategies.
Security Improvements: Ongoing research into mitigating vulnerabilities like Nothing at Stake has led developers toward implementing multi-layered security measures ensuring robustness against potential exploits.
Community Engagement & Governance: Many projects leverage token-holder voting rights embedded within protocols encouraging active community involvement—which fosters transparency but also raises questions about influence concentration among large stakeholders.
Why Understanding Proof-of-Stake Matters
For investors considering cryptocurrencies utilizing PoS algorithms—or developers designing next-generation blockchain solutions—it’s crucial understanding both benefits and limitations inherent within this mechanism:
- Recognizing how validator incentives align with network health helps assess long-term sustainability prospects;
- Being aware of centralization risks guides better governance structures;
- Monitoring ongoing developments ensures preparedness amidst evolving regulatory landscapes;4.. Appreciating technical nuances supports informed decision-making regarding project viability or investment potential.
By grasping these core aspects rooted deeply in cryptographic principles—and supported by real-world implementations—you can better navigate today’s rapidly changing blockchain environment grounded increasingly upon proof-based consensus models like Proof-of-Stake.
This overview provides clarity around what makes proof-of-stake an influential component within modern blockchain architecture—from foundational concepts through current trends—all essential knowledge whether you're an investor aiming for informed decisions or developer seeking innovative solutions rooted in proven technology principles
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
Understanding Blob-Carrying Transactions in Blockchain Sharding
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way digital assets and data are transferred, stored, and verified. As the popularity of blockchain networks grows, so does the need for scalable solutions that can handle increasing transaction volumes without compromising security or decentralization. One promising approach to achieving this scalability is through sharding, a technique that divides a blockchain network into smaller, manageable segments called shards. Within this framework, blob-carrying transactions have emerged as an innovative method to optimize data processing and improve overall network efficiency.
What Are Blob-Carrying Transactions?
Blob-carrying transactions are specialized data structures designed to facilitate efficient transaction processing within sharded blockchain networks. Unlike traditional transactions that are verified individually by each node across the entire network, blob-carrying transactions package multiple small transactions into a single large "blob." This blob acts as a container holding numerous individual operations or data points.
The primary purpose of these blobs is to reduce verification overhead on individual nodes. Instead of verifying each small transaction separately—which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive—nodes verify larger blobs containing many transactions at once. This process significantly decreases latency and increases throughput, enabling the network to handle more users and higher transaction volumes without sacrificing security.
How Do Blob-Carrying Transactions Enhance Blockchain Scalability?
In traditional blockchain systems like Bitcoin or early versions of Ethereum, every node must validate every transaction directly. While this ensures high security levels through full validation, it also limits scalability because nodes become bottlenecks under heavy loads.
Sharding addresses this issue by dividing the network into smaller segments—each shard processes its own subset of transactions independently. However, managing communication between shards introduces complexity; verifying cross-shard interactions efficiently becomes challenging.
Blob-carrying transactions help mitigate these challenges by:
- Reducing Verification Load: By bundling multiple small transactions into one blob per shard, nodes only need to verify fewer large data structures instead of numerous tiny ones.
- Streamlining Data Transfer: Blobs simplify cross-shard communication since they encapsulate multiple operations in a single package.
- Improving Network Throughput: With less verification overhead per node and optimized data handling within shards, overall transaction processing speeds increase dramatically.
This approach aligns with modern demands for high-performance blockchains capable of supporting decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, NFTs marketplaces—and other use cases requiring rapid confirmation times at scale.
Recent Advances in Sharding Using Blob-Carrying Transactions
Blockchain projects worldwide have been actively exploring sharding techniques incorporating blob-based methods:
Ethereum 2.0's Sharding Implementation: Ethereum's transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS) includes extensive sharding plans aimed at scaling its ecosystem sustainably. The Beacon Chain launched in December 2020 laid groundwork for future shard chains.
In September 2022, Ethereum activated its first phase of full sharding with the Shanghai hard fork—introducing parallel processing capabilities via shard chains that utilize blob-like structures for efficient validation.
Polkadot’s Interoperability Focus: Polkadot employs parachains—independent blockchains connected via relay chains—to facilitate seamless asset transfer across different networks.
Its architecture leverages sharded design principles where blobs enable quick cross-chain messaging while maintaining security guarantees.
Solana’s High Throughput Model: Solana adopts unique consensus mechanisms combining Proof-of-History (PoH) with Proof-of-Stake (PoS). It processes thousands of transactions per second using parallel execution similar to sharding concepts but optimized through innovative data structuring akin to blobs for batch validation purposes.
These developments demonstrate how integrating blob-like transactional models within sharded architectures can significantly enhance performance metrics such as throughput and latency while maintaining robust security standards essential for mainstream adoption.
Challenges Associated With Blob-Based Sharded Networks
Despite their advantages, implementing blob-carrying transactions within sharded systems presents several hurdles:
Security Concerns:
- Ensuring each shard remains secure against malicious actors is critical; if one shard becomes compromised due to inadequate validation protocols on blobs or faulty aggregation methods — it could threaten overall network integrity.
Interoperability Complexities:
- Facilitating smooth communication between different shards—or even disparate blockchains—is complex when relying on bundled transactional data like blobs because synchronization issues may arise if not managed properly.
User Experience Variability:
- As different shards may process batches differently or experience varying load levels during peak times—a user might notice inconsistent confirmation times depending on which part of the network their transaction interacts with.
Regulatory Considerations:
- As blockchain adoption expands into regulated sectors such as finance or healthcare—with strict compliance requirements—the design choices around batching mechanisms like blobs must align with legal standards concerning transparency and auditability.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research focused on enhancing cryptographic proofs associated with batch validations while developing standardized protocols ensuring interoperability without sacrificing decentralization principles.
The Future Role Of Blob-Carrying Transactions in Blockchain Ecosystems
As blockchain technology continues evolving towards greater scalability solutions—including Layer 2 rollups and other off-chain methods—blob-based approaches will likely remain integral components within broader architectural frameworks aimed at optimizing performance without compromising trustlessness or censorship resistance.
Furthermore:
- They will play vital roles in enabling real-time applications such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), gaming platforms requiring rapid state updates,
- Supporting enterprise-grade solutions where high throughput combined with privacy-preserving features is necessary,
- And facilitating interoperability initiatives among diverse ecosystems aiming toward unified multi-chain environments.
By improving how large datasets are packaged and validated efficiently across distributed ledgers—a core function served by blob-carrying transactions—they contribute substantially toward realizing scalable decentralized infrastructures suitable for mainstream adoption.
Key Takeaways About Blob-Carrying Transactions
To summarize:
- They bundle multiple small operations into larger "blobs" reducing verification overhead,
- Play an essential role in scaling efforts like Ethereum's upcoming upgrades,
- Enable faster cross-shard communication crucial for complex dApps,
- Present ongoing challenges related to security assurance & interoperability,
- Will continue shaping future multi-chain ecosystems aiming for high performance alongside robust decentralization standards.
Understanding how these advanced transactional techniques fit within broader scaling strategies provides valuable insights into building resilient yet efficient blockchain networks capable of supporting tomorrow’s digital economy needs.
Keywords & Semantic Terms Used:
Blockchain scalability | Sharded blockchain | Transaction batching | Cross-shard communication | Ethereum 2.0 | Polkadot parachains | Solana throughput | Distributed ledger technology | Decentralized applications (dApps) | Blockchain interoperability


kai
2025-05-14 12:35
What role do blob-carrying transactions play in sharding?
Understanding Blob-Carrying Transactions in Blockchain Sharding
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way digital assets and data are transferred, stored, and verified. As the popularity of blockchain networks grows, so does the need for scalable solutions that can handle increasing transaction volumes without compromising security or decentralization. One promising approach to achieving this scalability is through sharding, a technique that divides a blockchain network into smaller, manageable segments called shards. Within this framework, blob-carrying transactions have emerged as an innovative method to optimize data processing and improve overall network efficiency.
What Are Blob-Carrying Transactions?
Blob-carrying transactions are specialized data structures designed to facilitate efficient transaction processing within sharded blockchain networks. Unlike traditional transactions that are verified individually by each node across the entire network, blob-carrying transactions package multiple small transactions into a single large "blob." This blob acts as a container holding numerous individual operations or data points.
The primary purpose of these blobs is to reduce verification overhead on individual nodes. Instead of verifying each small transaction separately—which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive—nodes verify larger blobs containing many transactions at once. This process significantly decreases latency and increases throughput, enabling the network to handle more users and higher transaction volumes without sacrificing security.
How Do Blob-Carrying Transactions Enhance Blockchain Scalability?
In traditional blockchain systems like Bitcoin or early versions of Ethereum, every node must validate every transaction directly. While this ensures high security levels through full validation, it also limits scalability because nodes become bottlenecks under heavy loads.
Sharding addresses this issue by dividing the network into smaller segments—each shard processes its own subset of transactions independently. However, managing communication between shards introduces complexity; verifying cross-shard interactions efficiently becomes challenging.
Blob-carrying transactions help mitigate these challenges by:
- Reducing Verification Load: By bundling multiple small transactions into one blob per shard, nodes only need to verify fewer large data structures instead of numerous tiny ones.
- Streamlining Data Transfer: Blobs simplify cross-shard communication since they encapsulate multiple operations in a single package.
- Improving Network Throughput: With less verification overhead per node and optimized data handling within shards, overall transaction processing speeds increase dramatically.
This approach aligns with modern demands for high-performance blockchains capable of supporting decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, NFTs marketplaces—and other use cases requiring rapid confirmation times at scale.
Recent Advances in Sharding Using Blob-Carrying Transactions
Blockchain projects worldwide have been actively exploring sharding techniques incorporating blob-based methods:
Ethereum 2.0's Sharding Implementation: Ethereum's transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS) includes extensive sharding plans aimed at scaling its ecosystem sustainably. The Beacon Chain launched in December 2020 laid groundwork for future shard chains.
In September 2022, Ethereum activated its first phase of full sharding with the Shanghai hard fork—introducing parallel processing capabilities via shard chains that utilize blob-like structures for efficient validation.
Polkadot’s Interoperability Focus: Polkadot employs parachains—independent blockchains connected via relay chains—to facilitate seamless asset transfer across different networks.
Its architecture leverages sharded design principles where blobs enable quick cross-chain messaging while maintaining security guarantees.
Solana’s High Throughput Model: Solana adopts unique consensus mechanisms combining Proof-of-History (PoH) with Proof-of-Stake (PoS). It processes thousands of transactions per second using parallel execution similar to sharding concepts but optimized through innovative data structuring akin to blobs for batch validation purposes.
These developments demonstrate how integrating blob-like transactional models within sharded architectures can significantly enhance performance metrics such as throughput and latency while maintaining robust security standards essential for mainstream adoption.
Challenges Associated With Blob-Based Sharded Networks
Despite their advantages, implementing blob-carrying transactions within sharded systems presents several hurdles:
Security Concerns:
- Ensuring each shard remains secure against malicious actors is critical; if one shard becomes compromised due to inadequate validation protocols on blobs or faulty aggregation methods — it could threaten overall network integrity.
Interoperability Complexities:
- Facilitating smooth communication between different shards—or even disparate blockchains—is complex when relying on bundled transactional data like blobs because synchronization issues may arise if not managed properly.
User Experience Variability:
- As different shards may process batches differently or experience varying load levels during peak times—a user might notice inconsistent confirmation times depending on which part of the network their transaction interacts with.
Regulatory Considerations:
- As blockchain adoption expands into regulated sectors such as finance or healthcare—with strict compliance requirements—the design choices around batching mechanisms like blobs must align with legal standards concerning transparency and auditability.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research focused on enhancing cryptographic proofs associated with batch validations while developing standardized protocols ensuring interoperability without sacrificing decentralization principles.
The Future Role Of Blob-Carrying Transactions in Blockchain Ecosystems
As blockchain technology continues evolving towards greater scalability solutions—including Layer 2 rollups and other off-chain methods—blob-based approaches will likely remain integral components within broader architectural frameworks aimed at optimizing performance without compromising trustlessness or censorship resistance.
Furthermore:
- They will play vital roles in enabling real-time applications such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), gaming platforms requiring rapid state updates,
- Supporting enterprise-grade solutions where high throughput combined with privacy-preserving features is necessary,
- And facilitating interoperability initiatives among diverse ecosystems aiming toward unified multi-chain environments.
By improving how large datasets are packaged and validated efficiently across distributed ledgers—a core function served by blob-carrying transactions—they contribute substantially toward realizing scalable decentralized infrastructures suitable for mainstream adoption.
Key Takeaways About Blob-Carrying Transactions
To summarize:
- They bundle multiple small operations into larger "blobs" reducing verification overhead,
- Play an essential role in scaling efforts like Ethereum's upcoming upgrades,
- Enable faster cross-shard communication crucial for complex dApps,
- Present ongoing challenges related to security assurance & interoperability,
- Will continue shaping future multi-chain ecosystems aiming for high performance alongside robust decentralization standards.
Understanding how these advanced transactional techniques fit within broader scaling strategies provides valuable insights into building resilient yet efficient blockchain networks capable of supporting tomorrow’s digital economy needs.
Keywords & Semantic Terms Used:
Blockchain scalability | Sharded blockchain | Transaction batching | Cross-shard communication | Ethereum 2.0 | Polkadot parachains | Solana throughput | Distributed ledger technology | Decentralized applications (dApps) | Blockchain interoperability
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What Is a Vesting Schedule for Tokens?
Understanding the concept of a vesting schedule is essential for anyone involved in cryptocurrency projects, whether as an investor, developer, or stakeholder. At its core, a vesting schedule is a structured plan that determines how and when tokens are released to recipients over time. This mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring fair distribution, maintaining market stability, and aligning stakeholders’ interests with the long-term success of the project.
Why Token Vesting Matters in Blockchain Projects
Token vesting is more than just a technical detail; it’s a strategic tool used by blockchain projects to manage token supply and foster trust among investors and team members. When tokens are distributed without restrictions or schedules, it can lead to sudden sell-offs that destabilize the market or create perceptions of unfairness. Implementing vesting schedules helps mitigate these risks by controlling how quickly tokens enter circulation.
For investors and project teams alike, understanding how vesting works provides clarity on token availability and potential influence on market dynamics. It also demonstrates transparency from project developers—an important factor for regulatory compliance and building confidence within the community.
Types of Vesting Schedules
There are several common types of vesting schedules used across blockchain projects:
Linear Vesting: Tokens are gradually released at consistent intervals over the entire vesting period. For example, if 1 million tokens are vested over four years with monthly releases, approximately 20,833 tokens would be unlocked each month.
Cliff Vesting: A specific initial period (the "cliff") must pass before any tokens become available. After this cliff period—say six months—the remaining tokens start to unlock gradually or all at once.
Accelerated Vesting: Under certain conditions such as achieving milestones or during specific events like acquisitions or mergers, token release speeds up significantly compared to standard schedules.
These structures serve different strategic purposes: linear vestings promote steady engagement; cliffs protect early-stage projects from immediate sell-offs; accelerated options reward key achievements.
Key Components of Token Vesting Schedules
A typical vesting schedule incorporates several critical elements:
Vesting Period: The total duration over which tokens will be gradually released (e.g., 1 year, 4 years).
Cliff Period: An initial lock-up phase where no tokens are released until it ends (common durations range from three months to one year).
Release Intervals: The frequency at which vested tokens become accessible—monthly, quarterly, annually.
Vested Amounts: The portion of total allocated tokens that becomes available at each interval.
Some schedules include clawback provisions allowing projects to reclaim unvested tokens under certain circumstances—adding an extra layer of control but also complexity.
Regulatory Considerations for Token Vestings
As regulatory frameworks around cryptocurrencies evolve globally—and particularly within jurisdictions like the United States—the design of token vestings must adhere to legal standards. Agencies such as the SEC have issued guidance emphasizing transparency in token sales and distributions[1]. Properly structured vestings can help demonstrate compliance by showing that token allocations do not constitute unregistered securities offerings.
Projects should ensure theirvesting plans clearly specify timelines and conditions while avoiding practices that could be interpreted as manipulative or deceptive[5]. Transparent communication about these schedules builds trust among investors while reducing legal risks associated with non-compliance.
Recent Trends Enhancing Token Distribution Strategies
The industry has seen significant advancements in how vestings are implemented:
Use of smart contracts automates release processes based on predefined rules[3], increasing transparency and reducing manual errors.
Incorporation of performance metrics aligns token releases with project milestones rather than fixed timelines alone[2].
More sophisticated models now consider multiple factors such as team performance incentives alongside traditional time-based releases[2].
These innovations aim not only to improve fairness but also enhance stakeholder engagement by tying rewards directly to project achievements—a practice increasingly favored by regulators seeking accountability.
Risks Associated With Poorly Managed Vests
While well-designed schemes support healthy markets and stakeholder relations,poor management can have serious repercussions:
- Market Volatility:* If large amounts of vested tokens suddenly become available due to poorly planned schedules,it may flood exchanges causing price swings[4].
Legal Challenges: Non-compliance with jurisdictional regulations could lead to sanctions,legal action,or loss of credibility[5].
Stakeholder Distrust: Lackluster communication about unlocking timelines或 perceived unfairness might erode confidence,damaging long-term relationships within communities[6].
Therefore,careful planning combined with transparent disclosure is essential for safeguarding both project integrity和 investor interests。
How To Design an Effective Token Vestment Schedule
Creating an optimal schedule involves balancing multiple factors:
- Define clear goals:Determine whether your priority is long-term stability、team retention、or incentivizing milestones。
- Choose appropriate structure:Select between linear、cliff、or hybrid models based on your project's needs。
- Set realistic timelines:Align lock-up periods和 release intervals with development phases。
- Ensure regulatory compliance:Consult legal experts确保您的计划符合相关法律法规。
- Automate where possible:Utilize smart contracts来确保自动执行和透明度。
By carefully considering these aspects,你可以建立一个公平、安全且符合法规的vesting体系,为项目的持续成功奠定基础。
The Role Of Smart Contracts In Automating Vests
Smart contracts在现代区块链项目中扮演着关键角色。它们可以自动化token的释放过程,根据预设条件(如时间或达成特定目标)自动解锁tokens。这不仅提高了效率,还增强了透明度,因为所有操作都在区块链上公开记录,无需第三方干预。此外,这种自动化减少了人为错误和潜在的操控风险,使得整个vesting流程更加可信赖。
未来发展趋势显示,将智能合约与性能指标结合使用,将进一步优化token分发策略,实现更动态、更灵活的激励机制。这一技术进步也符合行业对安全性和合规性的不断追求,为投资者提供更有保障的环境。
References
1. SEC Guidance on Token Sales (2020)
2. Industry Trends in Vesting Schedules (2023)
3. Smart Contract-Based Vesting Schedules (2022)
4. Market Volatility Risks (2021)
5. Regulatory Risks in Token Distribution (2020)
6. Stakeholder Trust and Vesting Schedules (2022)
By understanding what a vestingat schedule entails—including its types、components、regulatory considerations以及最新行业趋势—you gain valuable insights into managing digital assets responsibly。 Whether you're developing new blockchain protocols或investors evaluating opportunities,这些知识都是确保安全、公平分配的重要基础。


kai
2025-05-14 08:42
What is a vesting schedule for tokens?
What Is a Vesting Schedule for Tokens?
Understanding the concept of a vesting schedule is essential for anyone involved in cryptocurrency projects, whether as an investor, developer, or stakeholder. At its core, a vesting schedule is a structured plan that determines how and when tokens are released to recipients over time. This mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring fair distribution, maintaining market stability, and aligning stakeholders’ interests with the long-term success of the project.
Why Token Vesting Matters in Blockchain Projects
Token vesting is more than just a technical detail; it’s a strategic tool used by blockchain projects to manage token supply and foster trust among investors and team members. When tokens are distributed without restrictions or schedules, it can lead to sudden sell-offs that destabilize the market or create perceptions of unfairness. Implementing vesting schedules helps mitigate these risks by controlling how quickly tokens enter circulation.
For investors and project teams alike, understanding how vesting works provides clarity on token availability and potential influence on market dynamics. It also demonstrates transparency from project developers—an important factor for regulatory compliance and building confidence within the community.
Types of Vesting Schedules
There are several common types of vesting schedules used across blockchain projects:
Linear Vesting: Tokens are gradually released at consistent intervals over the entire vesting period. For example, if 1 million tokens are vested over four years with monthly releases, approximately 20,833 tokens would be unlocked each month.
Cliff Vesting: A specific initial period (the "cliff") must pass before any tokens become available. After this cliff period—say six months—the remaining tokens start to unlock gradually or all at once.
Accelerated Vesting: Under certain conditions such as achieving milestones or during specific events like acquisitions or mergers, token release speeds up significantly compared to standard schedules.
These structures serve different strategic purposes: linear vestings promote steady engagement; cliffs protect early-stage projects from immediate sell-offs; accelerated options reward key achievements.
Key Components of Token Vesting Schedules
A typical vesting schedule incorporates several critical elements:
Vesting Period: The total duration over which tokens will be gradually released (e.g., 1 year, 4 years).
Cliff Period: An initial lock-up phase where no tokens are released until it ends (common durations range from three months to one year).
Release Intervals: The frequency at which vested tokens become accessible—monthly, quarterly, annually.
Vested Amounts: The portion of total allocated tokens that becomes available at each interval.
Some schedules include clawback provisions allowing projects to reclaim unvested tokens under certain circumstances—adding an extra layer of control but also complexity.
Regulatory Considerations for Token Vestings
As regulatory frameworks around cryptocurrencies evolve globally—and particularly within jurisdictions like the United States—the design of token vestings must adhere to legal standards. Agencies such as the SEC have issued guidance emphasizing transparency in token sales and distributions[1]. Properly structured vestings can help demonstrate compliance by showing that token allocations do not constitute unregistered securities offerings.
Projects should ensure theirvesting plans clearly specify timelines and conditions while avoiding practices that could be interpreted as manipulative or deceptive[5]. Transparent communication about these schedules builds trust among investors while reducing legal risks associated with non-compliance.
Recent Trends Enhancing Token Distribution Strategies
The industry has seen significant advancements in how vestings are implemented:
Use of smart contracts automates release processes based on predefined rules[3], increasing transparency and reducing manual errors.
Incorporation of performance metrics aligns token releases with project milestones rather than fixed timelines alone[2].
More sophisticated models now consider multiple factors such as team performance incentives alongside traditional time-based releases[2].
These innovations aim not only to improve fairness but also enhance stakeholder engagement by tying rewards directly to project achievements—a practice increasingly favored by regulators seeking accountability.
Risks Associated With Poorly Managed Vests
While well-designed schemes support healthy markets and stakeholder relations,poor management can have serious repercussions:
- Market Volatility:* If large amounts of vested tokens suddenly become available due to poorly planned schedules,it may flood exchanges causing price swings[4].
Legal Challenges: Non-compliance with jurisdictional regulations could lead to sanctions,legal action,or loss of credibility[5].
Stakeholder Distrust: Lackluster communication about unlocking timelines或 perceived unfairness might erode confidence,damaging long-term relationships within communities[6].
Therefore,careful planning combined with transparent disclosure is essential for safeguarding both project integrity和 investor interests。
How To Design an Effective Token Vestment Schedule
Creating an optimal schedule involves balancing multiple factors:
- Define clear goals:Determine whether your priority is long-term stability、team retention、or incentivizing milestones。
- Choose appropriate structure:Select between linear、cliff、or hybrid models based on your project's needs。
- Set realistic timelines:Align lock-up periods和 release intervals with development phases。
- Ensure regulatory compliance:Consult legal experts确保您的计划符合相关法律法规。
- Automate where possible:Utilize smart contracts来确保自动执行和透明度。
By carefully considering these aspects,你可以建立一个公平、安全且符合法规的vesting体系,为项目的持续成功奠定基础。
The Role Of Smart Contracts In Automating Vests
Smart contracts在现代区块链项目中扮演着关键角色。它们可以自动化token的释放过程,根据预设条件(如时间或达成特定目标)自动解锁tokens。这不仅提高了效率,还增强了透明度,因为所有操作都在区块链上公开记录,无需第三方干预。此外,这种自动化减少了人为错误和潜在的操控风险,使得整个vesting流程更加可信赖。
未来发展趋势显示,将智能合约与性能指标结合使用,将进一步优化token分发策略,实现更动态、更灵活的激励机制。这一技术进步也符合行业对安全性和合规性的不断追求,为投资者提供更有保障的环境。
References
1. SEC Guidance on Token Sales (2020)
2. Industry Trends in Vesting Schedules (2023)
3. Smart Contract-Based Vesting Schedules (2022)
4. Market Volatility Risks (2021)
5. Regulatory Risks in Token Distribution (2020)
6. Stakeholder Trust and Vesting Schedules (2022)
By understanding what a vestingat schedule entails—including its types、components、regulatory considerations以及最新行业趋势—you gain valuable insights into managing digital assets responsibly。 Whether you're developing new blockchain protocols或investors evaluating opportunities,这些知识都是确保安全、公平分配的重要基础。
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
Today’s Top Gainers:
$AITP/USDT: 129%
$VEL/USDT: 124%$PYTH/USDT : 80%
$JU Token is close to reach $22 a new ATH
#cryptocurrency #blockchain #finance
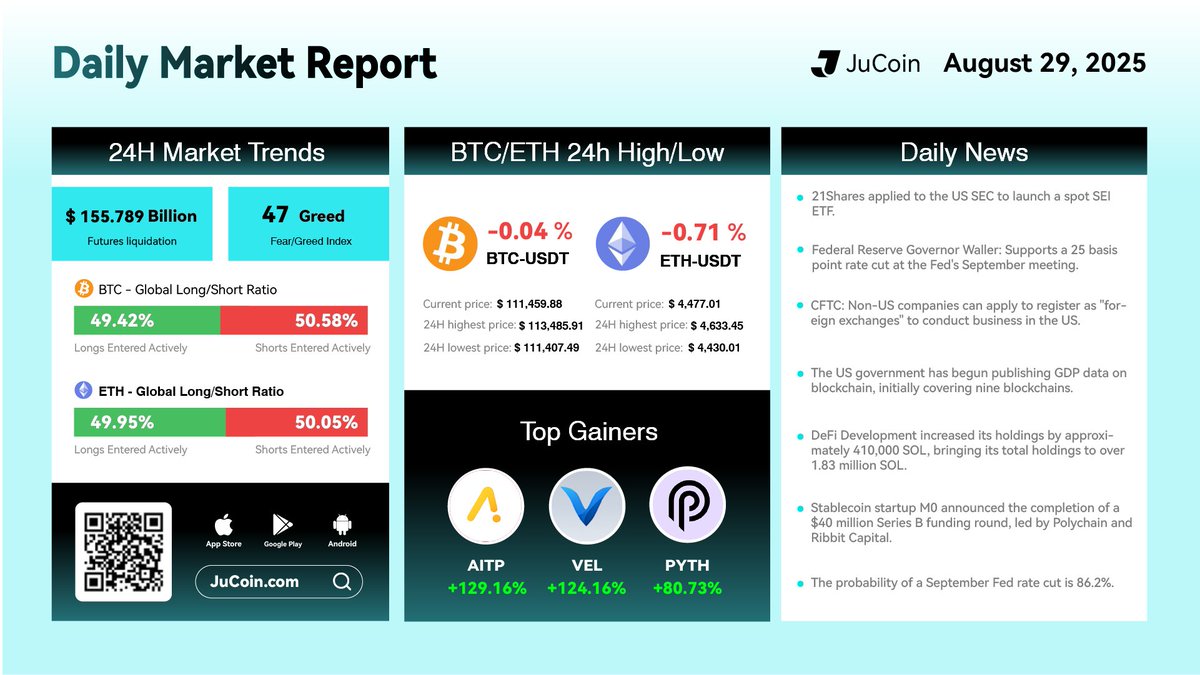


Mrconfamm
2025-08-29 07:37
Market Daily Report
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
Soit 111 milliards $ retirés du marché, accentuant la pénurie d’offre. La pression d’achat s’intensifie alors que le #Bitcoin devient de plus en plus rare. 🔥
#BTC #CryptoMarkets #cryptocurrency #blockchain
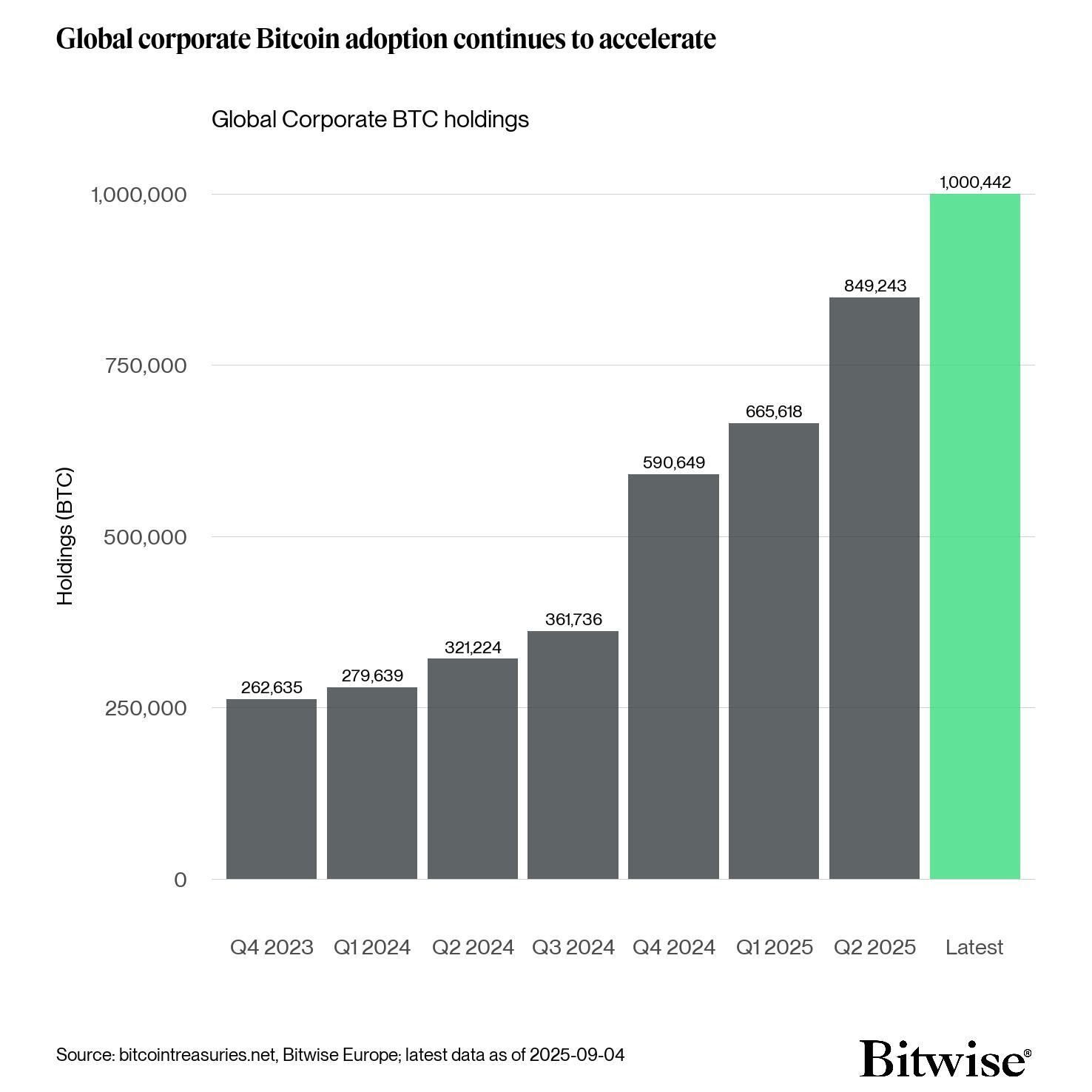


Carmelita
2025-09-04 21:53
🚨 Dernière minute : Les trésoreries d’entreprises mondiales franchissent le cap du 1M $BTC
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
How Does an Emergency Shutdown in MakerDAO Work?
Understanding the emergency shutdown process in MakerDAO is essential for anyone interested in decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contract security, or blockchain governance. This mechanism acts as a safety valve designed to protect the integrity of the protocol during critical threats. In this article, we will explore how this process functions, its significance within MakerDAO’s ecosystem, and recent developments that highlight its importance.
What Is MakerDAO and Its Role in DeFi?
MakerDAO is a pioneering decentralized lending platform built on Ethereum that enables users to generate DAI—a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar—without relying on traditional financial institutions. It operates through a set of smart contracts governed by MKR token holders who participate in decision-making via community votes. This decentralized governance model ensures transparency and collective control over protocol parameters.
The stability of DAI relies heavily on collateralized debt positions (CDPs) or vaults where users lock assets like ETH to mint new DAI tokens. Maintaining peg stability requires robust risk management mechanisms, including safeguards like emergency shutdown procedures.
Why Is an Emergency Shutdown Necessary?
In any complex system—especially one operating without centralized oversight—unexpected issues can arise. These might include security vulnerabilities, significant market shocks, or malicious attacks threatening user funds or system stability. The emergency shutdown feature provides a controlled way for the community to halt operations temporarily if such risks materialize.
This mechanism acts as an ultimate safeguard against catastrophic failures that could otherwise lead to loss of funds or systemic collapse. By enabling community-driven intervention through voting, MakerDAO emphasizes decentralization while ensuring rapid response capabilities when needed.
How Does the Emergency Shutdown Process Work?
The process involves several key steps designed for transparency and security:
1. Proposal Submission
Any member of the MakerDAO community can submit a proposal advocating for an emergency shutdown via official governance forums or voting portals. Such proposals typically outline specific reasons—like detected vulnerabilities—that justify halting operations temporarily.
2. Community Voting
Once submitted, proposals are subject to a voting period where MKR token holders cast their votes electronically within designated timeframes. To trigger an emergency shutdown successfully, it generally requires a supermajority vote—often around 80% approval—to prevent misuse or accidental activation.
3. Execution by Smart Contracts
If approved, the protocol's smart contracts automatically execute the shutdown sequence without human intervention beyond initial approval stages. This involves:
- Halting all new transactions related to collateral deposits and withdrawals.
- Disabling further minting or burning of DAI.
- Locking existing vaults until manual recovery procedures are initiated.
This automated execution minimizes delays and reduces potential points of failure during crises.
4. Post-Shutdown Recovery
Following activation, stakeholders work collectively on restoring normal operations by addressing underlying issues such as deploying patches for identified vulnerabilities or updating smart contracts with enhanced safeguards before re-enabling functionalities gradually.
Recent Incidents Highlighting Its Importance
MakerDAO’s emergency shutdown mechanism has been tested notably during high-profile security incidents—in particular August 2022 when vulnerabilities threatened millions worth of assets stored within its ecosystem.
During this event, swift community action led to initiating an emergency shutdown before attackers could exploit weaknesses fully—a move widely praised across DeFi circles as demonstrating effective governance responsiveness under pressure.
These incidents underscore how vital such safety features are; they serve not only as protective measures but also reinforce trust among users who rely on transparent risk mitigation strategies inherent in decentralized protocols.
Challenges and Debates Surrounding Emergency Shutdowns
While effective at safeguarding assets during crises, reliance on emergency shutdowns raises questions about operational continuity versus security risks:
- Over-reliance: Frequent use might suggest underlying systemic issues needing more permanent solutions rather than temporary halts.
- Governance Risks: Centralized decision-making power—even if distributed among MKR holders—could be misused if not properly checked.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As DeFi matures alongside traditional finance systems, regulators may scrutinize these mechanisms more closely due to their potential impact on financial stability and investor protection efforts.
Community discussions continue around balancing prompt crisis response with maintaining seamless service delivery—a core challenge faced by all decentralized protocols aiming for resilience without sacrificing decentralization principles.
Key Facts About MakerDAO’s Emergency Shutdown Mechanism
To summarize some critical aspects:
- The process is entirely driven by DAO governance through community votes.
- It can be triggered only after reaching predefined supermajority thresholds.
- Once activated, it halts all core activities within the ecosystem temporarily.
- The system enters a recovery phase focused on fixing issues before resuming normal operations.
Understanding these facts helps demystify how decentralization empowers communities while providing necessary safety nets against unforeseen events.
Future Outlook: Evolving Governance & Security Measures
As DeFi continues expanding rapidly—with increasing asset volumes and user adoption—the importance of robust risk management tools like emergency shutdowns becomes even clearer. Ongoing debates focus on improving automation reliability while enhancing transparency around decision processes so that stakeholders remain confident in protocol resilience.
Additionally,
- Protocol upgrades aim at reducing false alarms,
- Enhanced audit practices seek early detection,
- Community education emphasizes responsible participation,
all contributing toward building safer decentralized ecosystems capable of weathering future challenges effectively.
By grasping how makerdao’s emergency shutdown works—from proposal initiation through execution—you gain insight into one facet of sophisticated blockchain governance designed not just for innovation but also resilient risk mitigation within open financial systems worldwide.


kai
2025-05-14 13:08
How does an emergency shutdown in MakerDAO work?
How Does an Emergency Shutdown in MakerDAO Work?
Understanding the emergency shutdown process in MakerDAO is essential for anyone interested in decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contract security, or blockchain governance. This mechanism acts as a safety valve designed to protect the integrity of the protocol during critical threats. In this article, we will explore how this process functions, its significance within MakerDAO’s ecosystem, and recent developments that highlight its importance.
What Is MakerDAO and Its Role in DeFi?
MakerDAO is a pioneering decentralized lending platform built on Ethereum that enables users to generate DAI—a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar—without relying on traditional financial institutions. It operates through a set of smart contracts governed by MKR token holders who participate in decision-making via community votes. This decentralized governance model ensures transparency and collective control over protocol parameters.
The stability of DAI relies heavily on collateralized debt positions (CDPs) or vaults where users lock assets like ETH to mint new DAI tokens. Maintaining peg stability requires robust risk management mechanisms, including safeguards like emergency shutdown procedures.
Why Is an Emergency Shutdown Necessary?
In any complex system—especially one operating without centralized oversight—unexpected issues can arise. These might include security vulnerabilities, significant market shocks, or malicious attacks threatening user funds or system stability. The emergency shutdown feature provides a controlled way for the community to halt operations temporarily if such risks materialize.
This mechanism acts as an ultimate safeguard against catastrophic failures that could otherwise lead to loss of funds or systemic collapse. By enabling community-driven intervention through voting, MakerDAO emphasizes decentralization while ensuring rapid response capabilities when needed.
How Does the Emergency Shutdown Process Work?
The process involves several key steps designed for transparency and security:
1. Proposal Submission
Any member of the MakerDAO community can submit a proposal advocating for an emergency shutdown via official governance forums or voting portals. Such proposals typically outline specific reasons—like detected vulnerabilities—that justify halting operations temporarily.
2. Community Voting
Once submitted, proposals are subject to a voting period where MKR token holders cast their votes electronically within designated timeframes. To trigger an emergency shutdown successfully, it generally requires a supermajority vote—often around 80% approval—to prevent misuse or accidental activation.
3. Execution by Smart Contracts
If approved, the protocol's smart contracts automatically execute the shutdown sequence without human intervention beyond initial approval stages. This involves:
- Halting all new transactions related to collateral deposits and withdrawals.
- Disabling further minting or burning of DAI.
- Locking existing vaults until manual recovery procedures are initiated.
This automated execution minimizes delays and reduces potential points of failure during crises.
4. Post-Shutdown Recovery
Following activation, stakeholders work collectively on restoring normal operations by addressing underlying issues such as deploying patches for identified vulnerabilities or updating smart contracts with enhanced safeguards before re-enabling functionalities gradually.
Recent Incidents Highlighting Its Importance
MakerDAO’s emergency shutdown mechanism has been tested notably during high-profile security incidents—in particular August 2022 when vulnerabilities threatened millions worth of assets stored within its ecosystem.
During this event, swift community action led to initiating an emergency shutdown before attackers could exploit weaknesses fully—a move widely praised across DeFi circles as demonstrating effective governance responsiveness under pressure.
These incidents underscore how vital such safety features are; they serve not only as protective measures but also reinforce trust among users who rely on transparent risk mitigation strategies inherent in decentralized protocols.
Challenges and Debates Surrounding Emergency Shutdowns
While effective at safeguarding assets during crises, reliance on emergency shutdowns raises questions about operational continuity versus security risks:
- Over-reliance: Frequent use might suggest underlying systemic issues needing more permanent solutions rather than temporary halts.
- Governance Risks: Centralized decision-making power—even if distributed among MKR holders—could be misused if not properly checked.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As DeFi matures alongside traditional finance systems, regulators may scrutinize these mechanisms more closely due to their potential impact on financial stability and investor protection efforts.
Community discussions continue around balancing prompt crisis response with maintaining seamless service delivery—a core challenge faced by all decentralized protocols aiming for resilience without sacrificing decentralization principles.
Key Facts About MakerDAO’s Emergency Shutdown Mechanism
To summarize some critical aspects:
- The process is entirely driven by DAO governance through community votes.
- It can be triggered only after reaching predefined supermajority thresholds.
- Once activated, it halts all core activities within the ecosystem temporarily.
- The system enters a recovery phase focused on fixing issues before resuming normal operations.
Understanding these facts helps demystify how decentralization empowers communities while providing necessary safety nets against unforeseen events.
Future Outlook: Evolving Governance & Security Measures
As DeFi continues expanding rapidly—with increasing asset volumes and user adoption—the importance of robust risk management tools like emergency shutdowns becomes even clearer. Ongoing debates focus on improving automation reliability while enhancing transparency around decision processes so that stakeholders remain confident in protocol resilience.
Additionally,
- Protocol upgrades aim at reducing false alarms,
- Enhanced audit practices seek early detection,
- Community education emphasizes responsible participation,
all contributing toward building safer decentralized ecosystems capable of weathering future challenges effectively.
By grasping how makerdao’s emergency shutdown works—from proposal initiation through execution—you gain insight into one facet of sophisticated blockchain governance designed not just for innovation but also resilient risk mitigation within open financial systems worldwide.
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
💰 Jusqu’à 200 USDT / mois pour les créateurs crypto + un partenariat long terme garanti.
Si tu es crypto creator, influenceur ou content maker Web3, c’est TON moment d’entrer dans la cour des grands.
🎯 Pourquoi rejoindre ?
✔️ Cash rewards mensuels → pas d’attente, tu encaisses tous les mois ✔️ Partenariat premium → top 10 créateurs = Gold Creator Channel ✔️ Visibilité boostée → ton contenu poussé via les canaux officiels ✔️ Stabilité & croissance → revenus fixes, events exclusifs, collabs écosystème
🏆 Récompenses mensuelles : 1️⃣ 1st place → 200 USDT 2️⃣ 2nd–5th → 100 USDT chacun 3️⃣ 6th–10th → 50 USDT chacun ✨ Bonus newcomer → 10 USDT dès les tâches test réussies
🛠️ Comment ça marche ?
1️⃣ Inscris-toi (2–7 septembre) 2️⃣ 21 jours → crée 15 contenus originaux autour de JuCoin 3️⃣ Ton contenu est évalué (originalité, impact, engagement) 4️⃣ Gagne tes USDT + ton badge Gold Creator ✨
👉 Peu importe ton style (vidéo, thread, visuel, analyse), tant que c’est crypto + JuCoin, tu peux briller.
🔥 Low barrier, high rewards. Même un débutant bien guidé peut devenir un Gold Creator.
📌 Formulaire en ligne dispo dès le 2 septembre via le site JuCoin, Twitter & Telegram.
✨ Rejoins Ju Square maintenant et transforme ton talent en revenus réguliers.
La création crypto n’attend plus : tu crées, tu gagnes.
#JuSquare #CryptoCreators #Web3Community #cryptocurrency #blockchain



Carmelita
2025-09-02 18:43
Ju Square Creator Partnership Program est OFFICIELLEMENT lancé !
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What Are the Inherent Risks of Interacting with DeFi Protocols?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has emerged as a transformative force in the financial industry, offering innovative ways to lend, borrow, trade, and earn yields without traditional intermediaries. While DeFi provides increased accessibility and transparency, it also introduces a range of inherent risks that users must understand before engaging. This article explores these risks comprehensively to help users navigate the complex landscape of DeFi safely.
Understanding Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
At the core of DeFi protocols are smart contracts—self-executing code that automates financial transactions based on predefined rules. Although they enable trustless operations, smart contracts are susceptible to bugs and vulnerabilities. Historically significant incidents like the DAO hack in 2016 demonstrated how exploited vulnerabilities could lead to massive losses; approximately 3.6 million Ether were drained due to a reentrancy bug[1]. These vulnerabilities often stem from coding errors or overlooked edge cases during development. As smart contracts are immutable once deployed, fixing such issues post-launch can be challenging and costly.
To mitigate this risk, rigorous security audits by third-party firms are essential before deploying new protocols or updates. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and bug bounty programs incentivize community participation in identifying potential flaws early.
Liquidity Risks in Decentralized Pools
Liquidity is vital for smooth trading and borrowing activities within DeFi ecosystems. Many protocols rely on liquidity pools—collections of tokens supplied by users—to facilitate transactions without centralized order books[2]. However, these pools can face liquidity shortages during periods of high volatility or market downturns. Insufficient liquidity can lead to slippage—where trades execute at unfavorable prices—or even transaction failures.
For example, during sudden market crashes or large trades (known as "whale" movements), prices may swing sharply due to low liquidity levels[3]. Users participating in yield farming or providing liquidity should be aware that their assets might become illiquid if market conditions deteriorate unexpectedly.
Market Volatility Impact
Cryptocurrencies used within DeFi platforms are inherently volatile assets; their values can fluctuate dramatically over short periods[3]. Such volatility directly affects collateral valuations in lending protocols and impacts yield calculations for farmers earning interest or rewards. A sudden price drop could trigger liquidation events where collateral is sold off automatically at unfavorable rates—a process known as "liquidation risk."
This unpredictability underscores the importance for users engaging with leverage-based strategies or staking assets: they must closely monitor market trends and set appropriate risk parameters like collateralization ratios to avoid unexpected losses.
Regulatory Uncertainty Surrounding DeFi
The regulatory landscape for DeFi remains largely undefined globally[4]. Governments and regulators are increasingly scrutinizing decentralized platforms due to concerns about consumer protection, money laundering risks, tax evasion potential—and whether existing laws apply effectively within decentralized environments.
This ambiguity exposes users and platform operators to legal uncertainties; regulations could change abruptly leading to restrictions on certain activities or shutdowns of platforms altogether[4]. Staying informed about evolving legal frameworks is crucial for participants who wish to avoid unintended compliance violations while maintaining access.
Security Threats: Phishing & Hacks
Beyond technical vulnerabilities within smart contracts themselves lies an array of security threats targeting individual users’ funds[5]. Phishing attacks remain prevalent—attackers impersonate legitimate services via fake websites or emails designed specifically to steal private keys or seed phrases necessary for wallet access(5). Once compromised, hackers can drain user accounts instantly.
High-profile hacks such as Wormhole’s $320 million breach in 2022 highlight how security lapses at bridge infrastructure points pose significant risks [10], emphasizing that no component is immune from attack vectors targeting cross-chain interoperability solutions used widely across DeFi ecosystems.
Users should adopt best practices including multi-factor authentication (MFA), hardware wallets when possible—and always verify URLs—to reduce susceptibility toward phishing schemes [5].
Reentrancy Attacks: A Persistent Threat
Reentrancy attacks exploit specific vulnerabilities where malicious actors repeatedly call functions within a contract before previous executions complete[6]. This loophole allows attackers unauthorized access—potentially draining funds from affected protocols if not properly guarded against reentrant calls(6).
The infamous DAO hack was an early example illustrating this threat’s severity [1], prompting developers worldwide toward implementing safeguards like mutexes (mutual exclusions) into their codebases today [6].
Ensuring robust coding standards combined with formal verification methods significantly reduces reentrancy-related exploits' likelihood across new protocol deployments.
Front-Running & Sandwich Attacks Exploiting Transaction Ordering
In blockchain networks where transaction ordering isn’t strictly controlled by centralized authorities—the phenomenon known as front-running becomes problematic.[7] Traders with faster access may observe pending transactions via mempool data—and place their own orders ahead intentionally (“front-run”) —altering prices unfavorably for others(7).
Sandwich attacks take this further by placing one order just before a target trade while another immediately afterward—effectively “sandwiching” it—to manipulate asset prices temporarily.[7] These tactics undermine fair trading principles within DEXs like Uniswap but also pose financial risks for regular traders unfamiliar with such exploits.[7]
Mitigation strategies include implementing time-weighted average pricing mechanisms (TWAP)and utilizing privacy-preserving techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs where feasible .
Dependence on Oracles & Data Integrity Issues
Many advanced DeFi applications depend heavily on external data sources called “oracles” — which provide real-time information like asset prices,[8] interest rates,[8] etc., necessary for executing automated decisions accurately(8). However , inaccuracies stemming from faulty data feeds—or malicious manipulation—can cause severe miscalculations leading either into unwarranted liquidationsor incorrect payouts(8).
Protocols employing multiple independent oracle sources coupled with decentralization techniques aimto improve resilience against false data injection but cannot eliminate all associated risks entirely .
Navigating the Risks: Best Practices & Future Outlook
While inherent dangers exist across various facets—from technical bugs through regulatory shifts—the key lies in adopting comprehensive risk management strategies . Regularly auditing codebases , diversifying investments , employing secure wallets , staying updated about legal developments ,and understanding protocol mechanics form partof prudent engagement practices .
Recent developments indicate increased focus on enhancing security measures—including more rigorous audits post-hack incidents—as well as efforts towards clearer regulation frameworks aimed at protecting investors while fostering innovation . As the ecosystem matures—with improved standards around transparency,safety,and compliance—the overall safety profile will likely improve over time—but vigilance remains essentialfor all participants involvedin decentralized finance activities.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 08:07
What are the inherent risks involved in interacting with DeFi protocols?
What Are the Inherent Risks of Interacting with DeFi Protocols?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has emerged as a transformative force in the financial industry, offering innovative ways to lend, borrow, trade, and earn yields without traditional intermediaries. While DeFi provides increased accessibility and transparency, it also introduces a range of inherent risks that users must understand before engaging. This article explores these risks comprehensively to help users navigate the complex landscape of DeFi safely.
Understanding Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
At the core of DeFi protocols are smart contracts—self-executing code that automates financial transactions based on predefined rules. Although they enable trustless operations, smart contracts are susceptible to bugs and vulnerabilities. Historically significant incidents like the DAO hack in 2016 demonstrated how exploited vulnerabilities could lead to massive losses; approximately 3.6 million Ether were drained due to a reentrancy bug[1]. These vulnerabilities often stem from coding errors or overlooked edge cases during development. As smart contracts are immutable once deployed, fixing such issues post-launch can be challenging and costly.
To mitigate this risk, rigorous security audits by third-party firms are essential before deploying new protocols or updates. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and bug bounty programs incentivize community participation in identifying potential flaws early.
Liquidity Risks in Decentralized Pools
Liquidity is vital for smooth trading and borrowing activities within DeFi ecosystems. Many protocols rely on liquidity pools—collections of tokens supplied by users—to facilitate transactions without centralized order books[2]. However, these pools can face liquidity shortages during periods of high volatility or market downturns. Insufficient liquidity can lead to slippage—where trades execute at unfavorable prices—or even transaction failures.
For example, during sudden market crashes or large trades (known as "whale" movements), prices may swing sharply due to low liquidity levels[3]. Users participating in yield farming or providing liquidity should be aware that their assets might become illiquid if market conditions deteriorate unexpectedly.
Market Volatility Impact
Cryptocurrencies used within DeFi platforms are inherently volatile assets; their values can fluctuate dramatically over short periods[3]. Such volatility directly affects collateral valuations in lending protocols and impacts yield calculations for farmers earning interest or rewards. A sudden price drop could trigger liquidation events where collateral is sold off automatically at unfavorable rates—a process known as "liquidation risk."
This unpredictability underscores the importance for users engaging with leverage-based strategies or staking assets: they must closely monitor market trends and set appropriate risk parameters like collateralization ratios to avoid unexpected losses.
Regulatory Uncertainty Surrounding DeFi
The regulatory landscape for DeFi remains largely undefined globally[4]. Governments and regulators are increasingly scrutinizing decentralized platforms due to concerns about consumer protection, money laundering risks, tax evasion potential—and whether existing laws apply effectively within decentralized environments.
This ambiguity exposes users and platform operators to legal uncertainties; regulations could change abruptly leading to restrictions on certain activities or shutdowns of platforms altogether[4]. Staying informed about evolving legal frameworks is crucial for participants who wish to avoid unintended compliance violations while maintaining access.
Security Threats: Phishing & Hacks
Beyond technical vulnerabilities within smart contracts themselves lies an array of security threats targeting individual users’ funds[5]. Phishing attacks remain prevalent—attackers impersonate legitimate services via fake websites or emails designed specifically to steal private keys or seed phrases necessary for wallet access(5). Once compromised, hackers can drain user accounts instantly.
High-profile hacks such as Wormhole’s $320 million breach in 2022 highlight how security lapses at bridge infrastructure points pose significant risks [10], emphasizing that no component is immune from attack vectors targeting cross-chain interoperability solutions used widely across DeFi ecosystems.
Users should adopt best practices including multi-factor authentication (MFA), hardware wallets when possible—and always verify URLs—to reduce susceptibility toward phishing schemes [5].
Reentrancy Attacks: A Persistent Threat
Reentrancy attacks exploit specific vulnerabilities where malicious actors repeatedly call functions within a contract before previous executions complete[6]. This loophole allows attackers unauthorized access—potentially draining funds from affected protocols if not properly guarded against reentrant calls(6).
The infamous DAO hack was an early example illustrating this threat’s severity [1], prompting developers worldwide toward implementing safeguards like mutexes (mutual exclusions) into their codebases today [6].
Ensuring robust coding standards combined with formal verification methods significantly reduces reentrancy-related exploits' likelihood across new protocol deployments.
Front-Running & Sandwich Attacks Exploiting Transaction Ordering
In blockchain networks where transaction ordering isn’t strictly controlled by centralized authorities—the phenomenon known as front-running becomes problematic.[7] Traders with faster access may observe pending transactions via mempool data—and place their own orders ahead intentionally (“front-run”) —altering prices unfavorably for others(7).
Sandwich attacks take this further by placing one order just before a target trade while another immediately afterward—effectively “sandwiching” it—to manipulate asset prices temporarily.[7] These tactics undermine fair trading principles within DEXs like Uniswap but also pose financial risks for regular traders unfamiliar with such exploits.[7]
Mitigation strategies include implementing time-weighted average pricing mechanisms (TWAP)and utilizing privacy-preserving techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs where feasible .
Dependence on Oracles & Data Integrity Issues
Many advanced DeFi applications depend heavily on external data sources called “oracles” — which provide real-time information like asset prices,[8] interest rates,[8] etc., necessary for executing automated decisions accurately(8). However , inaccuracies stemming from faulty data feeds—or malicious manipulation—can cause severe miscalculations leading either into unwarranted liquidationsor incorrect payouts(8).
Protocols employing multiple independent oracle sources coupled with decentralization techniques aimto improve resilience against false data injection but cannot eliminate all associated risks entirely .
Navigating the Risks: Best Practices & Future Outlook
While inherent dangers exist across various facets—from technical bugs through regulatory shifts—the key lies in adopting comprehensive risk management strategies . Regularly auditing codebases , diversifying investments , employing secure wallets , staying updated about legal developments ,and understanding protocol mechanics form partof prudent engagement practices .
Recent developments indicate increased focus on enhancing security measures—including more rigorous audits post-hack incidents—as well as efforts towards clearer regulation frameworks aimed at protecting investors while fostering innovation . As the ecosystem matures—with improved standards around transparency,safety,and compliance—the overall safety profile will likely improve over time—but vigilance remains essentialfor all participants involvedin decentralized finance activities.
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.
What Is Sharding in Blockchain?
Sharding is a transformative scalability solution designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of blockchain networks. As blockchain technology gains widespread adoption, the need to process increasing numbers of transactions quickly and securely becomes critical. Sharding addresses this challenge by dividing the entire network into smaller, manageable segments called shards, each capable of processing transactions independently. This division allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly reducing congestion and improving overall throughput.
In essence, sharding enables a blockchain network to operate more like a distributed database rather than a single monolithic ledger. Each shard functions as its own mini-blockchain with its unique state and transaction history but remains interconnected within the larger network framework. This structure not only boosts transaction speeds but also helps in scaling blockchain solutions for real-world applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and enterprise solutions.
How Does Sharding Work in Blockchain Networks?
The core idea behind sharding involves splitting the workload across various smaller components—shards—that work concurrently. Each shard processes a subset of all transactions based on specific criteria such as user accounts or data types. For example, one shard might handle payment transactions while another manages smart contract interactions.
To maintain consistency across these independent shards, mechanisms like cross-shard communication are implemented. These protocols ensure that when users perform transactions involving multiple shards—say transferring assets from one account managed by one shard to another managed by different shards—the system can verify and record these operations accurately without compromising security or integrity.
Shards typically operate as separate blockchains known as "shard chains." They maintain their own states—such as account balances or smart contract data—and process their designated set of transactions independently before periodically syncing with other shards through consensus protocols designed for cross-shard validation.
Types of Sharding
There are primarily two types of sharding used in blockchain systems:
Horizontal Sharding: This approach divides the network based on transaction types or user groups—for instance, separating payment processing from smart contract execution.
Vertical Sharding: Here, data is partitioned based on storage needs or data categories—for example, storing different kinds of information (user profiles vs transactional logs) separately across various shards.
Both methods aim to optimize resource utilization while maintaining security and decentralization principles inherent in blockchain technology.
Benefits of Implementing Sharding
Implementing sharding offers several significant advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By distributing transaction loads across multiple shards, networks can handle many more operations per second compared to traditional single-chain architectures.
Reduced Transaction Fees: Faster processing times mean less congestion; consequently, users often experience lower fees during peak usage periods.
Improved Network Efficiency: Smaller nodes manage fewer tasks within each shard—they require less computational power and storage capacity—making participation easier for more validators.
Parallel Processing: Multiple parts of the network work simultaneously rather than sequentially; this parallelism accelerates overall throughput significantly.
These benefits make sharded blockchains suitable for large-scale applications where high speed and low latency are essential requirements.
Challenges Associated With Blockchain Sharding
Despite its promising potential, implementing sharding introduces complex technical challenges that must be addressed:
Inter-Shard Communication
Ensuring seamless communication between different shards is vital yet difficult. Transactions involving multiple shards require secure protocols that prevent double-spending or inconsistencies—a problem known as cross-shard communication complexity.
Consensus Mechanisms Across Multiple Shards
Traditional consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) are not inherently designed for multi-shard environments. Developing efficient consensus models that work reliably across numerous independent chains remains an ongoing research area within blockchain development communities.
Security Concerns
Dividing a network into smaller segments increases vulnerability risks; if one shard becomes compromised due to an attack or bug exploitation—a scenario called "shard takeover"—it could threaten the entire ecosystem's security integrity unless robust safeguards are implemented effectively throughout all parts of the system.
Standardization & Adoption Barriers
For widespread adoption beyond experimental phases requires industry-wide standards governing how sharded networks communicate and interoperate seamlessly. Without standardization efforts among developers and stakeholders worldwide—including major platforms like Ethereum—the risk exists that fragmentation could hinder progress rather than accelerate it.
Recent Developments in Blockchain Sharding Technology
Major projects have made notable strides toward integrating sharding into their ecosystems:
Ethereum 2.0 has been at the forefront with plans for scalable upgrades through its phased rollout strategy involving beacon chains (launched December 2020). The next steps include deploying dedicated shard chains alongside cross-shard communication protocols aimed at enabling Ethereum’s massive ecosystem to scale efficiently without sacrificing decentralization or security standards.
Polkadot employs relay chains connecting parachains—independent blockchains optimized for specific use cases—that communicate via shared security models facilitating interoperability among diverse networks.
Cosmos, utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithm architecture allows developers to create zones (independent blockchains) capable of interoperation within an overarching hub-and-spoke model similar to Polkadot’s relay chain approach.
Research continues globally exploring innovative techniques such as state sharding, which aims at optimizing how state information is stored across nodes—a crucial factor influencing scalability limits further improvements.
Potential Risks Impacting Future Adoption
While promising solutions exist today—and ongoing research promises even better approaches—the path forward faces hurdles related mainly to:
Security Risks: Smaller individual shards may become targets due to reduced validation power compared with full nodes operating on entire networks.
Interoperability Challenges: Achieving flawless interaction between diverse systems requires standardized protocols; otherwise fragmentation may occur leading toward isolated ecosystems instead of unified platforms.
Adoption Hurdles & Industry Standardization
Without broad agreement on technical standards governing cross-shard communications—as well as regulatory considerations—widespread deployment might slow down considerably despite technological readiness.
Understanding How Blockchain Scaling Evolves Through Sharding
As demand grows exponentially—from DeFi applications demanding rapid trades versus enterprise-level integrations requiring high throughput—the importance lies not just in creating faster blockchains but ensuring they remain secure against evolving threats while interoperable enough for global adoption.
By addressing current limitations through continuous innovation—in protocol design improvements like state sharing techniques—and fostering collaboration among industry leaders worldwide who develop open standards —the future landscape looks promising: scalable yet secure decentralized systems capable enough for mainstream use.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what sharding entails within blockchain technology: how it works technically; why it matters; what benefits it offers; what challenges lie ahead; along with recent advancements shaping its future trajectory—all aligned towards helping users understand both foundational concepts and cutting-edge developments effectively.


Lo
2025-05-15 02:38
What is sharding in blockchain?
What Is Sharding in Blockchain?
Sharding is a transformative scalability solution designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of blockchain networks. As blockchain technology gains widespread adoption, the need to process increasing numbers of transactions quickly and securely becomes critical. Sharding addresses this challenge by dividing the entire network into smaller, manageable segments called shards, each capable of processing transactions independently. This division allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly reducing congestion and improving overall throughput.
In essence, sharding enables a blockchain network to operate more like a distributed database rather than a single monolithic ledger. Each shard functions as its own mini-blockchain with its unique state and transaction history but remains interconnected within the larger network framework. This structure not only boosts transaction speeds but also helps in scaling blockchain solutions for real-world applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and enterprise solutions.
How Does Sharding Work in Blockchain Networks?
The core idea behind sharding involves splitting the workload across various smaller components—shards—that work concurrently. Each shard processes a subset of all transactions based on specific criteria such as user accounts or data types. For example, one shard might handle payment transactions while another manages smart contract interactions.
To maintain consistency across these independent shards, mechanisms like cross-shard communication are implemented. These protocols ensure that when users perform transactions involving multiple shards—say transferring assets from one account managed by one shard to another managed by different shards—the system can verify and record these operations accurately without compromising security or integrity.
Shards typically operate as separate blockchains known as "shard chains." They maintain their own states—such as account balances or smart contract data—and process their designated set of transactions independently before periodically syncing with other shards through consensus protocols designed for cross-shard validation.
Types of Sharding
There are primarily two types of sharding used in blockchain systems:
Horizontal Sharding: This approach divides the network based on transaction types or user groups—for instance, separating payment processing from smart contract execution.
Vertical Sharding: Here, data is partitioned based on storage needs or data categories—for example, storing different kinds of information (user profiles vs transactional logs) separately across various shards.
Both methods aim to optimize resource utilization while maintaining security and decentralization principles inherent in blockchain technology.
Benefits of Implementing Sharding
Implementing sharding offers several significant advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By distributing transaction loads across multiple shards, networks can handle many more operations per second compared to traditional single-chain architectures.
Reduced Transaction Fees: Faster processing times mean less congestion; consequently, users often experience lower fees during peak usage periods.
Improved Network Efficiency: Smaller nodes manage fewer tasks within each shard—they require less computational power and storage capacity—making participation easier for more validators.
Parallel Processing: Multiple parts of the network work simultaneously rather than sequentially; this parallelism accelerates overall throughput significantly.
These benefits make sharded blockchains suitable for large-scale applications where high speed and low latency are essential requirements.
Challenges Associated With Blockchain Sharding
Despite its promising potential, implementing sharding introduces complex technical challenges that must be addressed:
Inter-Shard Communication
Ensuring seamless communication between different shards is vital yet difficult. Transactions involving multiple shards require secure protocols that prevent double-spending or inconsistencies—a problem known as cross-shard communication complexity.
Consensus Mechanisms Across Multiple Shards
Traditional consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) are not inherently designed for multi-shard environments. Developing efficient consensus models that work reliably across numerous independent chains remains an ongoing research area within blockchain development communities.
Security Concerns
Dividing a network into smaller segments increases vulnerability risks; if one shard becomes compromised due to an attack or bug exploitation—a scenario called "shard takeover"—it could threaten the entire ecosystem's security integrity unless robust safeguards are implemented effectively throughout all parts of the system.
Standardization & Adoption Barriers
For widespread adoption beyond experimental phases requires industry-wide standards governing how sharded networks communicate and interoperate seamlessly. Without standardization efforts among developers and stakeholders worldwide—including major platforms like Ethereum—the risk exists that fragmentation could hinder progress rather than accelerate it.
Recent Developments in Blockchain Sharding Technology
Major projects have made notable strides toward integrating sharding into their ecosystems:
Ethereum 2.0 has been at the forefront with plans for scalable upgrades through its phased rollout strategy involving beacon chains (launched December 2020). The next steps include deploying dedicated shard chains alongside cross-shard communication protocols aimed at enabling Ethereum’s massive ecosystem to scale efficiently without sacrificing decentralization or security standards.
Polkadot employs relay chains connecting parachains—independent blockchains optimized for specific use cases—that communicate via shared security models facilitating interoperability among diverse networks.
Cosmos, utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithm architecture allows developers to create zones (independent blockchains) capable of interoperation within an overarching hub-and-spoke model similar to Polkadot’s relay chain approach.
Research continues globally exploring innovative techniques such as state sharding, which aims at optimizing how state information is stored across nodes—a crucial factor influencing scalability limits further improvements.
Potential Risks Impacting Future Adoption
While promising solutions exist today—and ongoing research promises even better approaches—the path forward faces hurdles related mainly to:
Security Risks: Smaller individual shards may become targets due to reduced validation power compared with full nodes operating on entire networks.
Interoperability Challenges: Achieving flawless interaction between diverse systems requires standardized protocols; otherwise fragmentation may occur leading toward isolated ecosystems instead of unified platforms.
Adoption Hurdles & Industry Standardization
Without broad agreement on technical standards governing cross-shard communications—as well as regulatory considerations—widespread deployment might slow down considerably despite technological readiness.
Understanding How Blockchain Scaling Evolves Through Sharding
As demand grows exponentially—from DeFi applications demanding rapid trades versus enterprise-level integrations requiring high throughput—the importance lies not just in creating faster blockchains but ensuring they remain secure against evolving threats while interoperable enough for global adoption.
By addressing current limitations through continuous innovation—in protocol design improvements like state sharing techniques—and fostering collaboration among industry leaders worldwide who develop open standards —the future landscape looks promising: scalable yet secure decentralized systems capable enough for mainstream use.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what sharding entails within blockchain technology: how it works technically; why it matters; what benefits it offers; what challenges lie ahead; along with recent advancements shaping its future trajectory—all aligned towards helping users understand both foundational concepts and cutting-edge developments effectively.
Penafian:Berisi konten pihak ketiga. Bukan nasihat keuangan.
Lihat Syarat dan Ketentuan.